Cyient has added a pre-built solution for managed firmware over-the-air (FOTA) updates as part of its CyientfIQTM innovation platform. It helps accelerates development of intelligent and connected products for its customers across industry.
With increasing use of connected and intelligent devices, it is imperative that devices are kept up to date for new features and technology changes. Historically, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have been addressing firmware update requirements through channels such as dealer networks, service centers, or field service engineers. With growing need for and frequency of firmware updates, OEMs are challenged with timely firmware update, cost of firmware update, and training firmware update channels in various upload/download systems.
As more and more devices become wirelessly connected, over-the-air (OTA) update of firmware is emerging as a quick and effective solution.
Cyient brings over two decades of experience in embedded systems, wearables and diagnostic equipment, and digital and IoT solutions and services for OEMs, fleet operators, and asset management firms in oil and gas, mining, construction, agriculture, medical, automotive, off-highway, rail, aerospace and defense industries.
Cyient’s CyientfIQTM FOTA solution addresses the following firmware update scenarios commonly faced by industries:
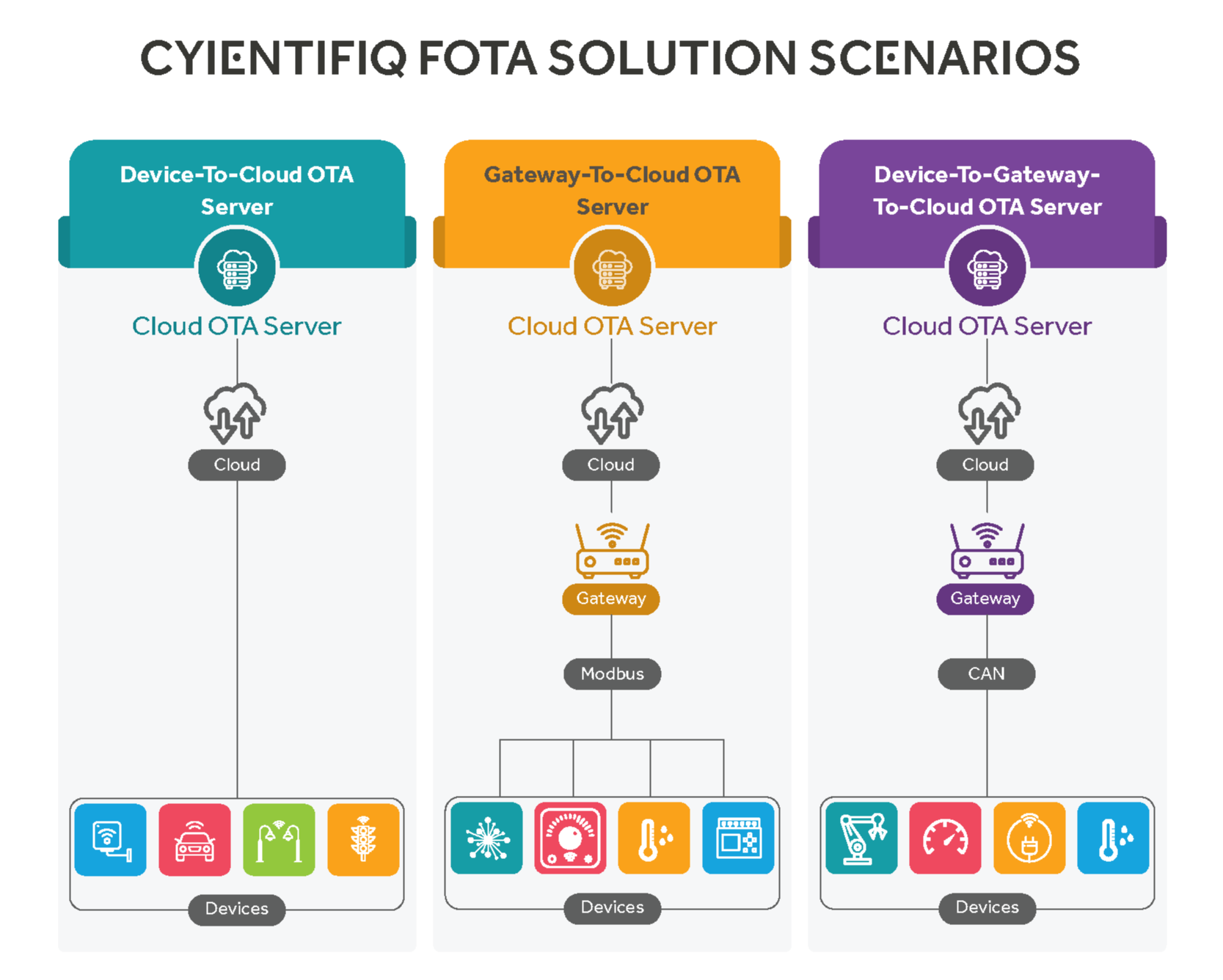
Device-to-cloud OTA server: Where the device is connected upstream to the Internet over 5G/LTE/Wi-Fi, it receives a complete or incremental firmware image update from the cloud OTA server. The microcontroller or the microprocessor and the associated peripherals in the device have the ability to carry out atomic update and automatic rollback (if needed) with minimal interruption of the device.
Gateway-to-cloud OTA server: Where the gateway is connected upstream to the Internet over 5G/LTE/Wi-Fi, it receives a complete or incremental firmware image update from the cloud OTA server. The microcontroller or the microprocessor and the associated peripherals have the ability to carry out atomic update and automatic rollback (if needed) with minimal interruption of the device. In this scenario, the devices that are connected downstream do not get a firmware update. Downstream devices such as temperature sensors or actuator controllers are less complex embedded systems, single function, and less prone to bug fixes or feature additions in their life time.
Device-to-gateway-to-cloud OTA server: Where the gateway is connected upstream to the Internet over 5G/LTE/Wi-Fi, it receives a complete or incremental firmware image update from the cloud OTA server for both gateway and the downstream devices connected to it. The gateway first completes its atomic update and auto rollback (if needed) with its new firmware image before it sends the right firmware image to the respective downstream devices over Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRA, Zigbee, Ethernet, CAN bus, or Profibus. Subsequently, each downstream device does the update with the new firmware image over industry standard communication protocol such as CAN. Downstream devices such as smart sensors, laser scan controllers, or embedded AI controllers are moderately or highly complex embedded systems, multi-function, and prone to frequent bug fixes or feature additions in their lifetime.
The CyientfIQTM FOTA solution is secure, reliable, and resilient for successfully delivering atomic updates and automatic rollback with minimal interruption of the device. The end-to-end FOTA update requires the coordination of complex elements right from the device, gateway, and device administration, to the cloud OTA server.
Device: If the device is connected upstream to the Internet, it fetches firmware from the cloud OTA server via application protocols such as MQTT, HTTP, or CoAP. Based on meta information, the device determines whether to update the firmware and disallows it if any improper firmware versions before the image are being downloaded into the secure memory location. However, if the device is connected upstream to the gateway, it fetches the firmware from the gateway via industry standard communication protocols such as CAN. Further, the device decrypts the image and verifies it before storing it into a secure memory location. The device reboots and launches the updated firmware image by a secure bootloader. Firmware update log messages and diagnostic data are sent to the device administrator via a gateway or direct as the case may be.
Gateway: The gateway communicates via application protocols such as MQTT, HTTP, or CoAP with the cloud OTA server to fetch the firmware image for update. Based on meta information, the gateway determines whether to update the firmware on gateway/device groups and disallows any improper firmware versions before the image is downloaded into a secure memory location. The gateway reboots and launches the updated firmware image with a secure bootloader. Firmware update log messages and diagnostic data are sent to the device administrator.
Device administration: This is responsible for uploading the update firmware binary along with configuration, diagnostic, and meta data to the smart FOTA cloud. It builds the firmware image and manifests, and enables scheduling of firmware updates to devices in groups. It keeps a record of update logs and diagnostic data. Cloud OTA server: Responsible for MQTT, HTTP, or CoAP server, and client services to read configurations, and store uploaded firmware binaries from the user. Also manages encryption, device keys, and security certificates such as SHA, AES, and TLS.
Secure update: Cybersecurity is paramount in a FOTA update. Security is addressed at each layer of the system architecture right from the device to the cloud OTA server:
Cyient provides customers a one-stop solution to implement their FOTA update strategy from device to cloud OTA server. Customers enjoy the following benefits from our FOTA update:
Cyient’s CyientfIQTM platform is a suite of reusable solution components to accelerate engineering development of intelligent products, connectivity solutions, and AI insights that prepares customers for the mega trends of the future. The FOTA solution on the CyientfIQTM platform is a reusable component for continuous and seamless update of these intelligent connected products.
Cyient (Estd: 1991, NSE: CYIENT)delivers Intelligent Engineering solutions for Digital, Autonomous and Sustainable Future
© Cyient 2024. All Rights Reserved.