- 2026-Feb-17
Two Sides of the Coin: Hype vs Reality in Autonomous Driving
Written by Shyamalendu Panda 01 Sep, 2023
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines 6 levels of driving automation ranging from 0 (fully manual) to 5 (fully autonomous). So, in 2009, when Google began testing its Autonomous cars on the streets of San Francisco, the automotive industry knew it had hit yet another milestone. Fast forward 14 years since then, modern day driving has been influenced by autonomy to such a scale, that several leading automotive manufacturers are pivoting towards offering features of conditional and high automation as a part of their core offerings.
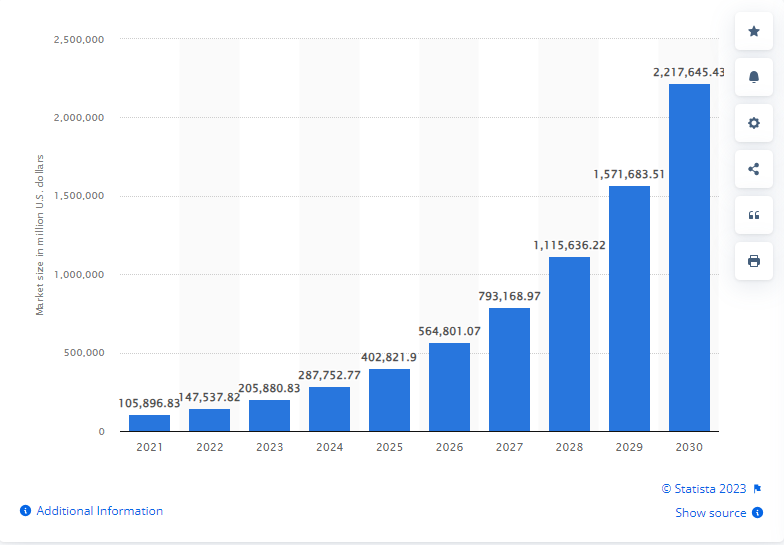
According to an autonomous vehicle market forecast by Next Move Strategy Consulting, the global autonomous vehicle market reached nearly the size of 106 billion U.S. dollars in 2021. It is projected that in 2030, the market will reach the size of over 2.3 trillion U.S. dollars.
New and evolving technologies that hold the potential to disrupt the automotive industry have found their place in the development of autonomous vehicles. A closer look into these technologies allows us to classify them across four primary categories:
Digitization: The digitization, including the use of advanced sensors, cameras, and other digital technologies to enable vehicles to perceive their environment and make decisions in real-time.
Increasing automation: Growing use of automation involves the use of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and other automated technologies that allow vehicles to function with little or no human intervention.
New business models: The emergence of new business models such as ride-sharing and car-sharing is also propelling the advancement of autonomous driving technologies. These new business models are opening up new avenues for the deployment of autonomous vehicles,particularly in metropolitan areas.
Connectivity: The rapid proliferation of connectivity is fueling the development of autonomous vehicles. This includes the use of advanced communication technologies, such as vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), to allow cars to share information and coordinate their movements in real time.
While the prospects of autonomous driving are undeniably promising, there are substantial challenges to surmount before widespread adoption can be realized. One of the main obstacles lies in the creation of reliable sensors endowed with precise environmental perception capabilities, capable of discerning objects under diverse weather conditions with utmost accuracy and reliability.
Similarly, another challenge lies in the task of developing algorithms proficient in analyzing the data gathered by these sensors and making swift, well-informed decisions across a diverse spectrum of scenarios. A comprehensive resolution to legal and regulatory concerns pertaining to responsibility, insurance, and the intricacies of "self-driving" is also imperative before autonomous driving can be fully embraced.
Despite the roadblocks, there has been significant progress in the field of autonomous driving. Major industry players such as Tesla, Audi, BMW, Bosch, and Waymo have invested considerably in pioneering autonomous driving technology, and numerous test programs are already underway, unveiling exciting advancements.
Weighing the pros and cons
Let’s not forget the benefits. Foremost among these advantages is the potential to considerably reduce traffic accidents by adhering strictly to traffic laws and minimizing distractions. Additionally, the seamless coordination and communication among autonomous cars promise improved traffic flow and reduced congestion, presenting an appealing prospect for urban areas grappling with traffic issues.
Moreover, autonomous vehicles hold the promise of enhanced mobility, particularly for individuals unable to drive themselves, such as the elderly and disabled, thereby elevating their autonomy and quality of life. All this notwithstanding the fact that embracing autonomous driving could contribute to a more eco-conscious transportation landscape, with potential reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the adoption of fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.
However, it is equally essential to recognize and address potential drawbacks associated with autonomous driving. Job losses in the transportation industry, affecting professions like truck drivers and taxi drivers, pose a significant socio-economic concern that necessitates careful attention.
As with any technology that relies heavily on digital systems, autonomous vehicles may face security risks. Threats like hacking and system malfunctions could lead to accidents or cause harm, necessitating robust safety measures and stringent protocols. Moreover, the vast data collection inherent to autonomous vehicles raises valid privacy concerns, underscoring the need for robust data protection frameworks.
Autonomous driving is here to stay. There is no denying it. It offers unprecedented possibilities for safety, efficiency, and accessibility. In order to achieve the true potential of this technology, automotive manufacturers, OEMs and other allied industries need to come together to acknowledge the challenges that lie ahead. Together, we can realize the captivating vision of a future where mobility is driven by technology.
With over three decades of expertise, Cyient brings the latest technologies to automotive OEMs and Tier-1s, creating a robust ecosystem that powers autonomous vehicle. Autonomous Vehicles - ADAS: Leveraging cloud-based infrastructure and digital connectivity to enable advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) in autonomous vehicles, enhancing safety and efficiency on the road.
About the Author
Shyamalendu Panda is the Industry Offer Head – Automotive & Mobility at Cyient. He has 19 years of experience in consultative technology selling of Engineering solutions for customers across multiple industries. In his current role, he is responsible for building Automotive industry specific Go-to Market Offers leveraging Embedded and Digital.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




