- 2026-Feb-17
Smart Packaging: Ushering Sustainability with Digitization
Written by Vijay Karna Mar 4, 2022 4:52:48 PM
Attractive packaging is a key factor in marketing products. While design can greatly enhance the appeal of the product, the primary functions of packaging are containment, protection, utility, usability, durability. Therefore, all these factors must be considered when selecting packaging. Digitalization can make packaging smart by being more efficient, reliable, and sustainable, as shown below.
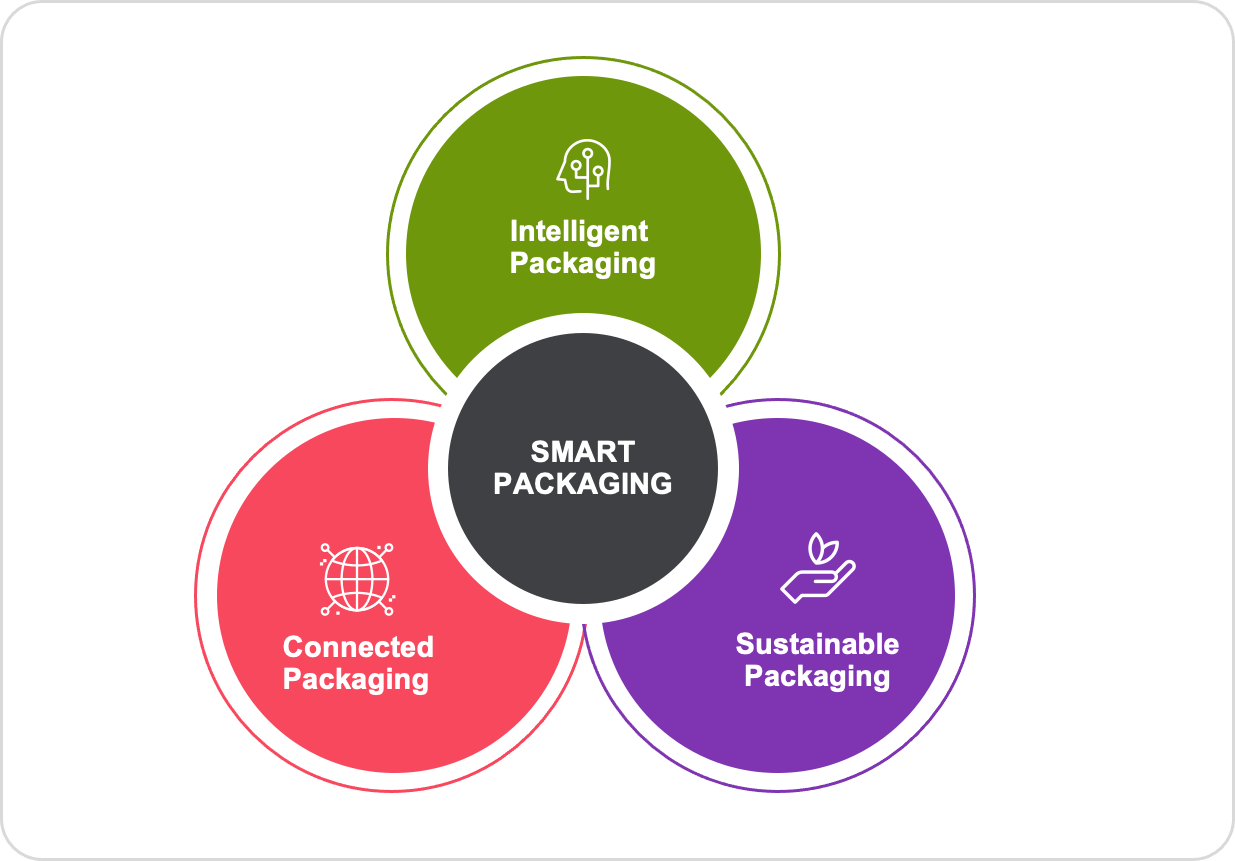
“Smart” packaging refers to packaging that leverages technology to provide functionality beyond simply housing or protecting products. Technology embedded in packaging usually provides information about the product or brand. Smart packaging is enabled by data analysis software for the packaging industry to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
The infographic below shows how smart packaging is advantageous in the food processing industry.
The use of intelligent packaging, especially for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical products, is one type of smart packaging. In intelligent packaging, sensors detect the freshness or temperature of package contents. Intelligent packaging helps embed the following indicators in packaging:
- Integrity Indicator: Senses leakage; for example, changes in packaging color can indicate bacterial growth, leaky packaging, or temperature disruption. Drug packaging with RFID chips, LEDs, and loudspeakers is now being used in the pharmaceutical industry to track pill removal and trigger an alarm if they have been taken incorrectly. With the use of chips, package inserts can be read and reordered on smartphones.
- Damage/Freshness Indicator: Quality assurance would be greatly enhanced by an indicator that specifically shows the deterioration of the product over time in addition to packages leaking or temperatures being compromised.
Connected packaging helps in every retail product category, from toys and cosmetics to gaming and apparel. The packaging of a connected product is printed with a special code. Mobile devices can be used to activate the code for exclusive content for consumers. Connected packaging helps increase the net promoter score (NPS) and customer satisfaction index (CSI). For example, customers can scan the code on the package to visit the company website and unlock a series of exclusive online video tutorials to learn more about the product and usage. This helps in the activation rate, with a return user base and increased website traffic. Connected packaging also helps in predicting the remaining shelf life of the product and comparison with similar products along with ratings.
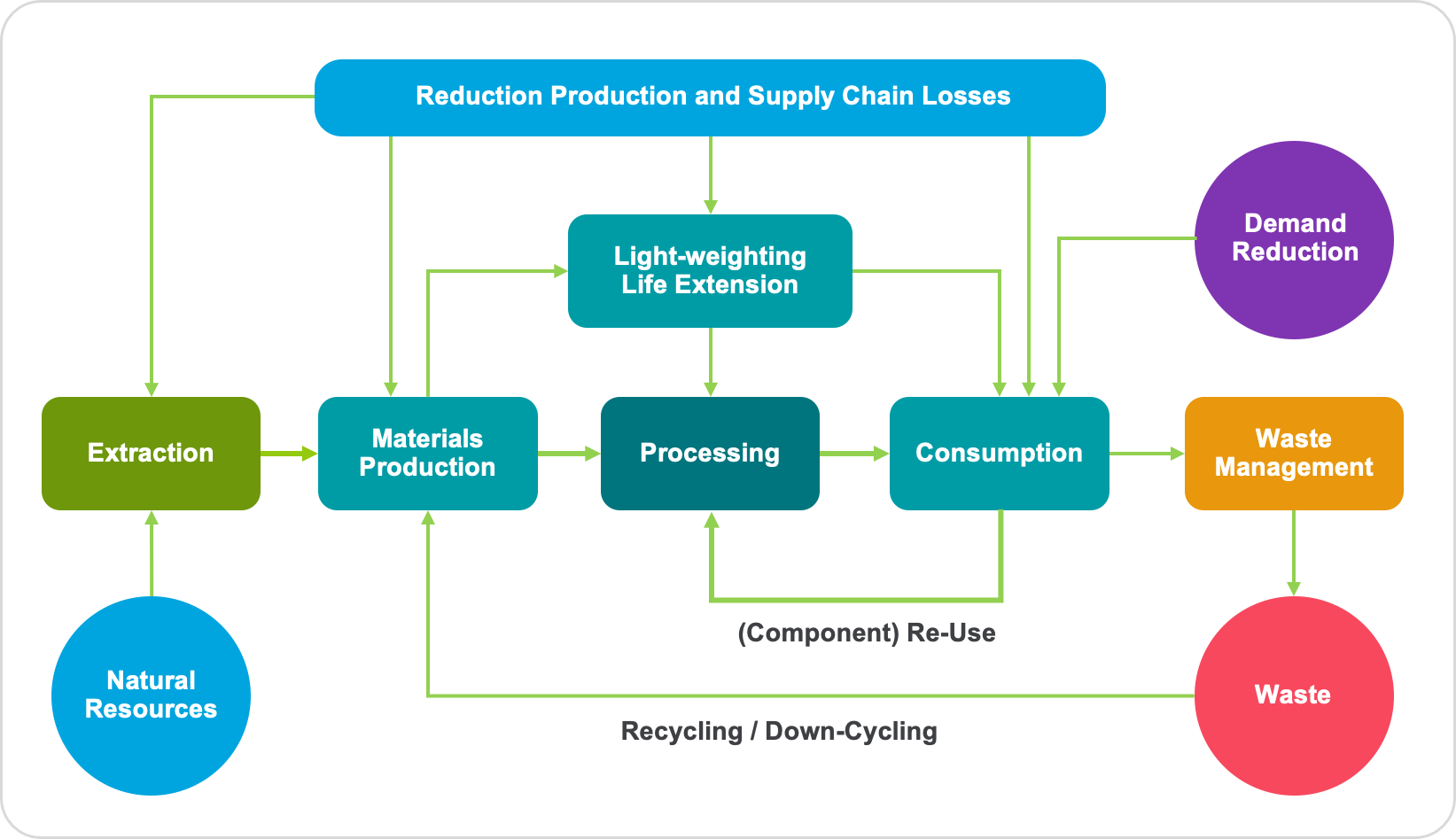
With both government and consumers increasingly focusing on environmental impact and sustainability, packaging firms are rethinking their responsibility toward sustainable packaging. Using circular economy business models, companies create a positive social impact, decouple economic activity from the consumption of finite resources, and design waste out of the system. The vast majority of packaging is designed to be used and discarded in a linear process, resulting in enormous waste and pollution. The current waste disposal system is convenient for consumers, who are not charged for the waste, but it is a highly inefficient use of materials. In order to move toward more sustainable packaging, it is important to consider the entire life cycle of a product and its packaging so that the whole system becomes circular by design. By facilitating this, companies can stay ahead of tighter regulations, expand their growth prospects, and reduce their environmental impact. Companies whose business models rely on products that are destined for obsolescence or do not adapt to reuse will likely suffer the most from this slow but steady shift toward a circular economy, so also those that provide feedstock for the production of new plastic, such as fossil fuel companies.
The diagram below explains the concept of sustainable packaging.
To know more about smart packaging and how CYIENT can help in the digitalization of packaging, please visit Intellicyient
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




