- 2026-Feb-17
Designing Medical Devices for Emerging Markets
Written by Brian Wyatt Oct 3, 2016 1:43:04 PM
According to the International Monetary Fund, emerging and developing economies like Brazil, Russia, India, China, Mexico, and Saudi Arabia contributed 70% of the global economic growth in 2015. Collectively, these countries also account for the largest population (4.37 billion) in the world, representing a significantly underserved market. A closer look at the markets in these countries show us that they have a primarily upwardly-mobile middle-tier population that demands cost-effective services and products.
Demands for better and price-sensitive healthcare in these countries is on the rise. Fueled by the three main problems of an aging population, cost-effective healthcare, and high patient volumes, the Healthcare industry is undergoing rapid changes and developments. For example, according to the US consulting firm Strategy & (formerly Booz & Company), pharmaceutical sales doubled in emerging markets such as the BRICS countries between 2006 and 2011.
While upcoming local companies (focused on innovation) are creating products with local materials at affordable prices, there is huge potential for established global companies to capitalize on these markets. Building on their manufacturing expertise, device makers have to rethink efficiencies and cost savings for a successful concept-to-market product cycle to enter these markets – they need to find new ways to meet local demands of technology, utility, and costs.
The only way to innovate is to go back to the drawing board and undertake a detailed design of the product range, look for opportunities to eliminate excess cost, and gain flexibility to sell profitably in price-sensitive markets. This exercise involves some interesting challenges like changing economies, currency fluctuations, growing competition, lack of understanding in terms of affordability, accessibility, and country-specific operational protocols, etc.
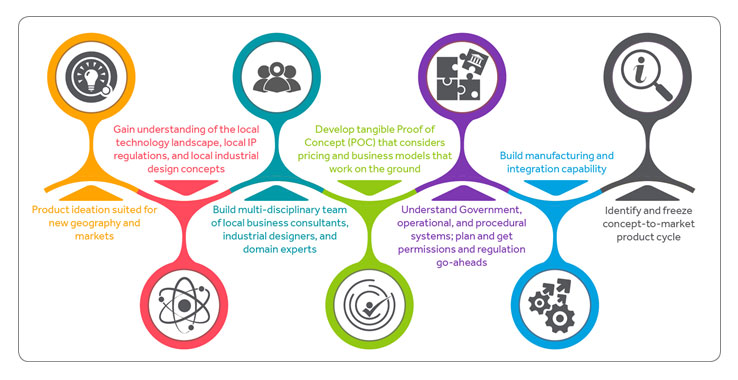
So what are the things medical device companies need to consider? In my experience, the top seven considerations for international device makers include:
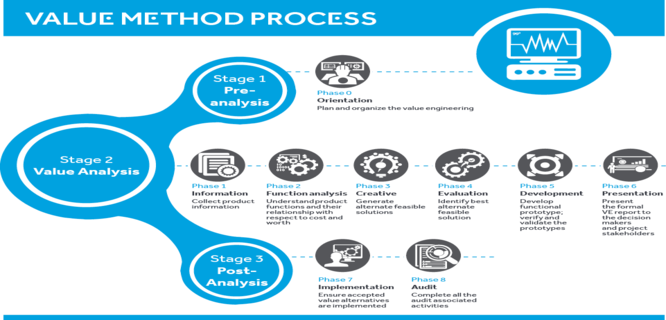
Synonymous with the terms value management, value methodology and value analysis (since it contains similar characteristics) VE is a professionally applied, function-oriented, systematic team approach used to analyze and improve value in a product, facility design, system or services. VE is a powerful industry standard for solving problems and reducing costs while improving performance and quality requirements. At its core, VE uses rational logic, a step-by-step process of why and how questioning, and analysis of product functions and performance to identify relationships that may increase value.
Device makers can regain control over their costs by not only assessing these costs, but also systematically classifying and identifying them. The intent is to produce conclusions that note areas of possible optimization and remove unnecessary expenditures through alternate solutions. Using a systematic approach to perform cost reduction not only yields improvement but provides decision-makers with rationalized trade-offs involved in achieving these efforts.

For the medical device industry, VE techniques can yield relatively quick results in product cost reduction while leaving as much of the core product the same to prevent the need for a 510(k) premarket notification, CE Mark or other regulatory requalification. While OEM's may not have the required expertise and/or bandwidth to undertake this exercise, many have found it advantageous to identify and work closely with a service provider who can manage this process in a structured way:
In the short term, the ROI associated with value engineering will continue to evolve on two parallel streams; overcoming intense margin pressure in established markets and developing products that are viable in underserved, price-sensitive emerging markets. More and more, as products developed for the emerging markets show equal or improved patient outcomes at significantly lower cost, the opportunity to disrupt more established markets will become much more prevalent. We'll cover that concept, known as 'reverse innovation', in a subsequent blog post.
What are your views on the value, future, and challenges of value engineering? Please use the comments section below to drop in your views.
Dig Deeper:
- Whitepaper: Value Engineering: Assessing Costs, Quality, and performance
- Brochure: Harnessing the Power of Value Engineering
- About Cyient's Manufacturing Engineering Competency
- About Cyient's Medical Technology & Healthcare services
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




