- 2026-Feb-17
How the Modern Electric Utility is Growing: From Data to Big Data Analytics
Written by Tareg Ghaoud Aug 31, 2020 4:31:52 PM
Improving network planning, operation, asset maintenance, and making informed decisions are critical to modern utilities to achieve better efficiency and a high level of customer satisfaction. The study of data within the utility network has a vital role to play in enabling insights-led decision-making for more Distributed Energy Resources (DER) connections, improving the network reliability and critical asset maintenance processes.
As utility data becomes more substantial in volume driven by smart meter rollouts, increased installations of Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), sensors at secondary substations, and other unstructured data, the need for data analytics, more so big data analytics, increases.
With multiple sources of origin, the data collected, transferred, managed, and analyzed by a utility is not always structured as the case with traditional data analytics platforms. Add to this the complexity of the difference in speed of data collection, transfer, management, and analyses. An example of such high-speed analytic application is in the study of the social media conversations where the utility may need to use that data as an input in the prediction of coming storms.
Therefore, the transformation from data to big data platforms in utilities is necessary due to the change in the characteristics of the data (4Vs: Volume, Variety, Velocity, and Value). The traditional architectures of using data warehouses with relational databases do not work effectively when the data becomes “big.” For this reason, utilities need to be open to consider big data platforms if they wish to do more advanced grid analytics to get a faster response and enable more business and operational insights in managing their smart grid networks
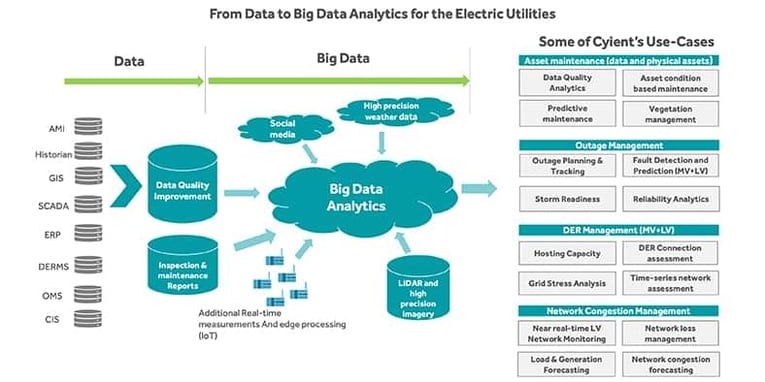
A tailored, big data platform will help utilities in going beyond traditional business intelligence. It will boost decision-making capabilities by filtering, condensing, and analyzing bigger data sets at speeds faster than before.
For more information on how utilities can overcome their data challenges and apply techniques to build a bespoke grid analytics platform, as well as generate use cases on how the platform brings real results, download our white paper.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




