Intelligent Engineering
Our Intelligent Engineering solutions across products, plant and networks, combine our engineering expertise with advanced technologies to enable digital engineering & operations, develop autonomous products & platforms, and build sustainable energy and infrastructure
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)
Revolutionizing Utilities Asset Management with Asset Performance ManagementAPM reduces unplanned downtime, maintenance costs, EHS risks, and enhances asset performance.
CyientRevolutionizing Utilities Asset Management with Asset Performance ManagementAPM reduces unplanned downtime, maintenance costs, EHS risks, and enhances asset performance.
Abstract
This white paper discusses the challenges utilities face in asset management. It highlights how Asset Performance Management (APM) provides an integrated, connected enterprise solution that enables utilities to bring disparate data sources together to find new trends and insights. This enables safer, more reliable operations while facilitating optimal performance at a lower sustainable cost. Cyient has partnered with IBM to leverage IBM’s APM software to help customers build an integrated, connected enterprise solution on APM. This helps utility companies expand asset operational efficiency, minimize environmental impact, and improve asset reliability, robustness, and efficiency of power grids and other utility infrastructure.
Introduction
Cyient, a global engineering and technology solutions company, has joined forces with IBM, a global leader in asset management and cognitive solutions provider, to offer cutting-edge and tailor-made solutions to customers for managing physical enterprise assets effectively and efficiently in the utilities, energy, manufacturing, transportation, aviation, and mining sectors.
These solutions include Enterprise Asset Management (EAM), which helps customers optimize the life cycle of their assets, reduce operational costs, and improve asset reliability; Asset Performance Management (APM), which leverages data analytics and artificial intelligence to monitor, predict, and prevent asset failures; Envizi Sustainability, which helps customers reduce their environmental impact and achieve their sustainability goals; weather and vegetation management, which helps customers mitigate the risks of weather-related disruptions and vegetation encroachment on their assets; and data-related solutions, which help customers harness the power of data to gain insights, improve decision-making, and enhance performance.
This white paper focuses on the features and business value that asset performance management brings to asset-heavy utility organizations in the face of increasing market competition and regulatory compliance.

Asset Management Maturity and Key Terms
The strategic approach and maturity level of an organization's asset management are pivotal factors in shaping the maintenance strategy, especially for asset-intensive sectors such as utilities.
The image below illustrates various maturity levels of asset management practiced in asset
Definition of Frequently Used Terms:
Reactive Maintenance
also known as corrective maintenance or breakdown maintenance, involves addressing issues and repairing assets only when they fail or show signs of malfunction. This approach relies on responding to unexpected breakdowns and fixing problems as they occur. It does not involve planned inspections or maintenance activities. It may seem cost-effective in the short term, but often leads to higher downtime, emergency repairs, and overall costs in the long run.
Run to Failure Maintenance
is a strategy where assets are operated until they break down completely, and only then are repairs or replacements initiated. This may be suitable for non-critical or easily replaceable assets where the cost of preventive maintenance outweighs the cost of occasional replacements. However, it can lead to unpredictable downtime and potential production losses.
Condition-Based Maintenance
involves real-time monitoring of the condition of equipment through various technologies (sensors, data analysis) and performing maintenance when specific conditions or thresholds are met. It aims to optimize maintenance efforts, reduce unnecessary tasks, and extend asset life by responding to actual equipment condition. It requires effective monitoring systems and data analysis capabilities.
Preventive Maintenance
encompasses systematically scheduled activities such as inspections, servicing, and component replacements. These tasks are carried out at predetermined intervals, guided by either frequency or usage considerations, in alignment with the asset's original equipment manufacturer (OEM) guidelines and the organization’s maintenance strategy. It aims to reduce downtime, extend asset lifespan, and lower overall maintenance costs. However, it requires careful planning and may involve some costs associated with performing maintenance tasks that might not be immediately necessary.
Predictive Maintenance
involves using data and advanced analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing for maintenance activities to be scheduled just in time. It relies on real-time monitoring, sensor data, and predictive analytics to anticipate issues before they lead to breakdowns. It aims to optimize maintenance schedules, minimize downtime, and reduce unnecessary maintenance tasks. However, it requires sophisticated monitoring systems and data analysis capabilities.
Prescriptive Maintenance
takes predictive maintenance a step further by not only predicting failures but also recommending specific actions to address identified issues. This proactive approach enables utilities to optimize maintenance strategies, reduce downtime, and extend asset lifespan, resulting in significant cost savings over time. It improves asset reliability and operational efficiency by providing actionable insights and recommendations based on predictive analytics. By implementing recommended maintenance actions, utilities can mitigate risks, enhance asset reliability, and optimize performance across their infrastructure.
Challenges for Enterprise Asset-Intensive Organizations
Asset-intensive organizations including utilities face the following primary challenges in asset management:
Complexity
Organizations often have a large number of assets to manage spread across multiple locations, sometimes in remote places, which can make it difficult to keep track of them all.
Data Management
These organizations generate a large amount of data, which can be difficult to manage and analyze. This data includes information about asset operations, performance, maintenance history, and other key metrics. Managing this data effectively is critical to optimize asset performance.
Managing Cost
Organizations must manage costs associated with asset management, including maintenance costs, repair costs, and replacement costs. Managing these costs effectively is critical to maintaining profitability.
Regulatory Compliance
Asset-intensive organizations must comply with a range of regulations related to asset management, including safety and environmental regulations. Ensuring compliance with these regulations can be a challenge.
Access Whitepaper
Problem Definition
To address these challenges, asset-intensive utility companies have built “asset journeys” that define use cases across the life cycle of each asset, using a suitable Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) solution to implement processes. This has enabled them to optimize and streamline asset operations, maintenance and repair, and inventory management processes, and extend asset life, reduce operational cost, and asset downtime.
Drawbacks in Traditional Asset Management Solutions
Traditional EAM has limitations in maximizing the asset performance, as it lacks the following features:
Real-time Asset Monitoring
EAM does not track the current status and condition of the assets, which can lead to inefficiencies and breakdowns.
Asset Health and Failure Prediction
EAM does not use data and analytics to assess the health and risks of the assets, which can result in unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Predictive and Prescriptive Based Maintenance
EAM does not provide optimal maintenance schedules and recommendations based on the asset performance and condition, which can reduce the asset life cycle and increase the maintenance costs.
Data-driven Analytics
EAM does not leverage the power of data and analytics to optimize the asset management process, which can improve the asset reliability, availability, and productivity.
High-Level Solution
The limitations of traditional asset management are overcome by the introduction of the Asset Performance Management (APM) solution.
The diagram below summarizes how APM is different from the traditional EAM solution.
Asset performance management is an integrated and data-driven approach that enables utilities to optimize the performance and reliability of their physical assets.
Key benefits of APM, absent in traditional asset management solutions, are:
Predictive Analytics
APM leverages advanced analytics and predictive modeling to forecast equipment failures and performance issues. While traditional asset management solutions may rely on historical data and reactive approaches, APM enables organizations to proactively address potential problems before they lead to failures.
Condition-Based Monitoring
APM integrates real-time monitoring and sensor data to assess the current condition of assets. Traditional asset management solutions often rely on fixed schedules for inspections and maintenance, while APM allows for condition-based monitoring, optimizing maintenance activities based on the actual health of assets.
Asset Health Visibility
APM provides a comprehensive view of asset health, combining historical data, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics. Traditional solutions may lack the depth of insights provided by APM, making it challenging to assess overall asset health and make informed decisions.
Optimized Maintenance Strategies
APM helps in developing maintenance strategies that are tailored to the specific needs and conditions of each asset. Traditional asset management solutions may use generic or fixed maintenance plans, whereas APM optimizes strategies based on asset criticality, performance history, and real-time condition monitoring.
Enhanced Reliability and Availability
APM leverages advanced analytics and predictive modeling to forecast equipment failures and performance issues. While traditional asset management solutions may rely on historical data and reactive approaches, APM enables organizations to proactively address potential problems before they lead to failures.
Risk-based Decision-making
APM enables utilities to make risk-informed decisions by assessing the impact and consequences of asset failures. Traditional asset management approaches may not incorporate a comprehensive risk assessment, leading to suboptimal decision-making in terms of asset maintenance and reliability.
Life Cycle Cost Optimization
APM focuses on optimizing the total life cycle cost of assets, considering acquisition, maintenance, and decommissioning. Traditional solutions may not holistically address the entire life cycle, potentially leading to higher overall costs.
Addressing Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance often requires utilities to maintain detailed documentation and regularly submit reports to regulatory authorities. APM solutions automate the documentation process, ensuring that all relevant data, maintenance records, and performance metrics are accurately recorded and easily accessible for regulatory audits. Traditional solutions do not have a comprehensive reporting mechanism as they lack breath and width of the data as compared to APM solutions.
Managing Complex Assets
Complex assets in utility industries often require continuous monitoring and diagnostics to identify potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. APM solutions leverage real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to monitor asset performance, detect anomalies, and provide actionable insights for timely, proactive maintenance. Traditional asset management solutions lack the capability to capture health information for complex assets and offer actionable insights.
IT/OT Integration
APM facilitates the integration of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) systems for a holistic view of asset performance. Traditional asset management solutions may operate in silos, limiting the ability to leverage data from both IT and OT systems.
Solution Details
Many utilities perform asset maintenance schedules purely on time intervals or usage-based data, taking critical assets such as transformers out of service frequently for maintenance, parts replacement, or even complete asset replacement. APM brings the concepts of condition monitoring, asset health scoring, predictive forecasting, and prescriptive maintenance. APM allows utilities to use a better approach such as asset condition, asset health score, and asset failure prediction for its critical assets to determine the maintenance and asset replacement strategy.
APM enables utilities to increase their reliability and reduce their operations and maintenance costs by shifting from a time-based to a performance-based maintenance strategy.
Cyient has partnered with IBM to leverage a suite of IBM Maximo solutions called the Maximo Asset Performance Management (Maximo APM) solution. This solution aims to help utility customers improve the overall performance of their critical assets, reduce maintenance costs, and minimize downtime.
Maximo Asset Performance Management (APM) Solution Pack for Utilities
This section details the various components of the Maximo Asset Performance Management (APM) solutions and their usage.
Maximo APM solution components are part of the IBM Maximo Application Suite (MAS). The Maximo APM pack consists of the following applications:
| Maximo Monitor | Maximo Health | Maximo Predict | Maximo Health and Predict – Utilities |
|---|
Maximo APM is a comprehensive suite of applications for asset monitoring, asset health tracking, predictive maintenance, and reliability planning. IBM Maximo APM is designed to help utilities get the most value from their enterprise assets. It offers advanced analytics that deliver greater insights so that utilities can take the best actions to optimize assets. The platform provides a comprehensive view of assets across the enterprise, and AI monitoring facilitates condition-based maintenance that can resolve issues before they happen. IBM Maximo APM can be operated on premises or on any cloud using the Red Hat OpenShift run-anywhere module.
Maximo Monitor
This is a logical starting point for building the APM solution as utilities begin moving to a new operating model. It provides real-time visibility of the condition of assets, with configurable dashboards, automatic anomaly detection, and alerts. It is designed to connect, store, analyze, monitor, and manage data, and can be used to monitor and manage data from a variety of sources, including legacy systems, historians , IoT sensors, and other repositories.
Business users can visualize current and historical trend data for their devices and assets in customizable dashboards. In the hierarchal navigator, users can drill down through layers from a system-wide view to individual assets. Analytic functions are applied to input data, and the output is displayed on value cards, tables, images, line graphs, and alert tables. The data is marked up with alert information that is driven from built-in anomaly detector models and alert functions.
Maximo Asset Monitor Includes the Following Components:
- • Platform component for connecting and registering devices.
- • Data stores for intermediate and long-term storage of data.
- • Analytics for performing calculations, anomaly detection, and alerts.
- • Configurable dashboards for monitoring KPIs, anomalies, and alerts.
Solution Capabilities and Business Value
Capabilities
- • Easily configurable dashboard: no-code widgets
- • Enterprise-wide view of operation
- • Workflow to drive ownership of issues
- • Auto-generation of work orders
- • Rapid data integration
- • Scalable dashboard filtering and management
Business Value
- • Reduce unplanned downtime by over 10%
- • Shorten duration of outages by over 50%
- • Increase production output by up to 5%
- • Decrease time wasted in investigating false-positive alerts
Maximo Health
Maximo Health is a suite of applications that helps manage the health of assets by using IoT data from asset sensors and other sources, such as the weather, asset details, and maintenance and repair history to increase asset availability and help in replacement planning.
It enables a consolidated, global view of critical assets with insights from data analytics to make smarter decisions about managing and maintaining assets. Operational technology data from Maximo Monitor, and information technology data from an enterprise asset management system are used to build health scores in Maximo Health.
Solution Capabilities and Business Value
Capabilities
- • Dashboard with cards, map view, spreadsheet view
- • Asst fleet-wide view and health drilldown
- • Health-based notifications and actions
- • Flexible health scoring by asset type or groups
- • Sensor data integration
- • Suggest refurbish / replace prioritization
Business Value
- • Reduce asset fleet-wide operational risk by focusing on the right assets
- • Increase asset availability
- • Reduce unnecessary preventive maintenance
- • Reduce time to make capital replacement planning decisions
Maximo Predict
Maximo Predict leverages historical and near-real-time asset performance data, maintenance records, inspection reports, and environmental data to correlate performance factors that predict asset degradation or failure.
Maximo Predict uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to predict future failures and values related to asset performance.
Maximo Predict can Calculate Predicted Values, such as:
- • Estimated time to failure for an asset.
- • The probability of a failure occurring in a selected prediction window (e.g., coming three months).
- • The historical trend of failure probability scores for an asset.
- • The probability of end-of-life failure for an asset anomaly that has occurred.
- • The trend of asset health anomaly scores for an asset over time.
Solution Capabilities and Business Value
Capabilities
- • Templates to build common predictive models
- • Score predictive models using Watson ML
- • View pre-built visualizations
- • Workflow for managing assets
- • Work queues for managing and tracking actions
Business Value
- • Reduced failures
- • Reduced maintenance costs
- • Improved asset utilization
- • Extended life of asset
- • Increased production output
Maximo Health and Predict – Utilities
Maximo Health and Predict – Utilities is built on Maximo Health and Predict, and includes pre-built analytics models based on industry standards that can be extended. They include risk and criticality scoring, health scoring, and degradation models. Common utilities asset models include: transformers, circuit breakers, switchgear, overhead / underground cables etc
Maximo Health and Predict – Utilities shares the same user interface (UI) as Health and Predict, and the utilities information will not appear unless Health and Predict – Utilities is installed, and the user is logged in as a premium user.
Solution Capabilities and Business Value
Capabilities
- • Dashboard with cards, map view, spreadsheet view
- • Fleet-wide view and health drilldown
- • Flexible health, criticality, effective age, end-of-life and risk scoring by asset type or groups
Business Value
- • Reduce operational risk by focusing on the right assets
- • Increase asset availability
- • Reduce unnecessary preventive maintenance
- • Reduce time to make capital replacement planning decisions
Note (Maximo Product Information):
Starting with Maximo Application Suite version 8.11, Maximo Health and Predict - Utilities is no longer available as a separate industry solution. The information that is provided is applicable only to Maximo Application Suite version 8.10 and earlier versions.
The Maximo Models for Electrical Distribution Accelerator replaces Maximo Health and Predict - Utilities in Maximo Application Suite version 8.11.
Conclusion
According to the Utility Analytics Institute (UAI), a significant impediment that persists is related to culture and change management. For many utilities, technology isn’t the problem. Most vendors can solve any technical problem they encounter. However, operationalizing the output of APM through effective change management is the challenge, and this needs to be addressed effectively by vendors in collaboration with the customer. Implementing and relying on APM requires a change in the way utilities have always done things. Utilities now need to think about asset risks in the same way they think about operational risks and set up a diagnostic center where work can be prioritized and assets can be monitored in real time.
5G technology in agriculture
The advent of 5G technology will revolutionize global farming landscapes and will open up multiple ways to establish and grow precision farming. The figure below shows that every element in modern agriculture once connected to a high speed and high throughput 5G cellular network, works in tandem with the other to optimize resources and maximize yield. The imagery generated from SAR and GPR demand throughput for transferring them to a distant and central location/data cloud. Similarly, to control farming equipment remotely, a low latency communications network in inevitable.
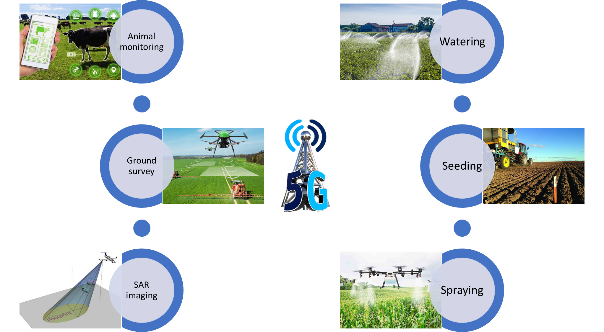
Figure 10. Uses of 5G technology in agriculture
Future of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation will continue to evolve and redefine industries. Here are a few trends that could shape its future:
Hyperautomation as-a-service
Cloud-based hyperautomation platforms will become more accessible, allowing organizations of all sizes to leverage automation as a service. This democratization of technology will drive innovation across sectors.
Human-automation collaboration
Rather than replacing humans entirely, hyperautomation will focus on enhancing human capabilities.
Industry-specific solutions
Hyperautomation will be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries. We can expect specialized solutions in sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, telecom, energy, and utilities addressing industry- specific challenges and requirements.
Enhanced cognitive capabilities
Advances in AI, ML, and Gen AI will lead to even more sophisticated cognitive capabilities, enabling systems to handle complex decision-making and problem- solving tasks.
IoT integration
IoT will become more tightly integrated with hyperautomation. Sensors and data from connected devices will be used to optimize and automate processes in real time.
Cross-industry collaboration
Industries will increasingly collaborate and share best practices for hyperautomation implementation. This cross-pollination of ideas will accelerate innovation and adoption.
Regulatory frameworks
Governments and regulatory bodies will establish frameworks to address the ethical and legal implications of hyperautomation, ensuring a responsible and fair use of the technology.
In the future, we can expect to see even more changes in the way hyperautomation is used and implemented. Advances in IoT, blockchain, and quantum computing will open opportunities for hyperautomation to be applied in new domains and enable it to automate highly complex tasks and processes.
About the Author
Pankaj Sahu spearheads the enterprise asset management (EAM) practice for electric, gas, and water utility technology solutions at Cyient. With a wealth of experience spanning over 20 years, he has an established track record in implementing and consulting EAM and APM solutions for clients in the utility, transportation, and energy sectors worldwide.
About Cyient
Cyient (Estd: 1991, NSE: CYIENT) partners with over 300 customers, including 40% of the top 100 global innovators of 2023, to deliver intelligent engineering and technology solutions for creating a digital, autonomous, and sustainable future. As a company, Cyient is committed to designing a culturally inclusive, socially responsible, and environmentally sustainable Tomorrow Together with our stakeholders.
For more information, please visit www.cyient.com