-
 Electric Vehicle Design & Development: Challenges, Next-generation Technologies and TrendsAddressing Key Hurdles While Harnessing Innovation for the Next Leap in EV Development.- Dr. Rajanand Patnaik Narasipuram
Electric Vehicle Design & Development: Challenges, Next-generation Technologies and TrendsAddressing Key Hurdles While Harnessing Innovation for the Next Leap in EV Development.- Dr. Rajanand Patnaik Narasipuram
electrification@cyient.com
Abstract
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is undergoing a transformative shift driven by the need for sustainable and innovative transportation solutions. This whitepaper explores the multifaceted challenges and groundbreaking advancements in EV design and development. Key areas of focus include high production costs, limited charging infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, and supply chain disruptions. Additionally, next-generation technologies such as advanced battery technology, power electronics, smart charging solutions, and vehicle-to- anything (V2X) capabilities are examined. By addressing these challenges and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, the EV industry aims to enhance performance, reduce costs, and improve accessibility. Strategic approaches, including public-private partnerships, government incentives, and sustainable supply chains, play a critical role in accelerating EV adoption.
Cyient's expertise in end-to-end EV design and development - including EE architecture, integration, cost optimization, powertrain engineering, charging systems, and technology integration - positions it as a leader in the transition to electric mobility, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Introduction
The EV industry is at the cusp of a significant transformation, driven by the relentless pursuit of innovation and sustainability. Next-generation EV development, characterized by modular architectures and commonization, is revolutionizing transportation by enhancing performance, efficiency and affordability. As governments worldwide push for carbon neutrality and reduced emissions EVs emerge as a pivotal solution.
Despite advancements challenges such as high production costs, limited charging infrastructure, evolving regulations, and supply chain constraints hinder rapid adoption.
This paper explores these challenges while examining cutting-edge technologies - advanced batteries, power electronics, and V2X capabilities to enhance performance, reduce costs, and improve accessibility, paving the way for a sustainable and efficient transportation future.

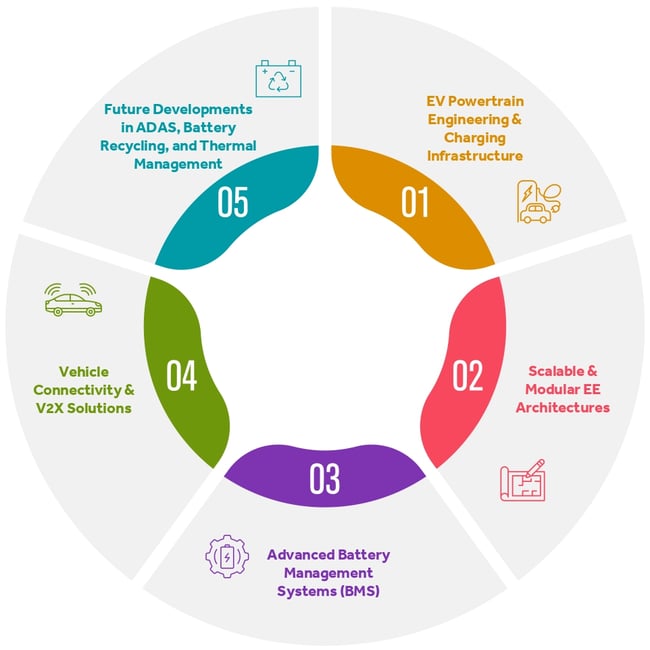
Challenges in EV Development
The development of electric vehicles presents a complex set of challenges that impact affordability, infrastructure, regulations, and supply chains. While EVs offer a sustainable alternative to traditional combustion-engine vehicles, overcoming these obstacles is essential to achieving widespread adoption and long-term viability.
High Production Costs
- EV production costs remain higher than internal combustion-engine (ICE) vehicles due to expensive battery technology and raw material constraints.
- Battery costs, despite reductions over the years, still constitute a significant portion of EV pricing.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
- Varying global safety standards, emissions regulations, and certification requirements create challenges for EV manufacturers.
- Compliance with stringent battery recycling and environmental impact regulations adds complexity.
Limited Charging Infrastructure & Range Anxiety
- The global charging infrastructure remains inadequate, particularly in rural and developing regions.
- Slow charging speeds and inconsistent availability contribute to consumer hesitation.
Supply Chain and Raw Material Shortages
- Dependency on critical raw materials (lithium, cobalt, nickel) makes the EV industry vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
- The push for localized and sustainable supply chains remains a work in progress.

Consumer Adoption Barriers
- Concerns around battery longevity, charging infrastructure, and higher upfront costs deter some buyers.
- Limited awareness of EV incentives and long-term cost benefits further slows adoption.
Technological Integration and Compatibility Issues
- The transition to advanced EE architectures and software-driven systems requires seamless integration across components. Compatibility issues between EVs and smart grids impact the efficiency of vehicle-to- grid (V2G) solutions.
Market Competition and Brand Differentiation
- The EV market is becoming increasingly competitive, with numerous manufacturers vying for market share.
- Differentiating products and building strong brand identities are essential for success in this crowded market.
Product Design and Optimization
- Designing and optimizing EVs to meet performance, safety, and cost requirements is a complex task.
- Engineers must balance various factors, including battery placement, thermal management, and aerodynamics, to create efficient and reliable vehicles.
Development Costs
- The high costs associated with research, development, and production of EVs pose a significant challenge.
- Manufacturers must invest heavily in new technologies and infrastructure, which can strain financial resources and impact profitability.
As a trusted innovation partner, Cyient continues to push the boundaries of EV development, accelerating the shift towards cleaner, smarter, and more connected electric mobility solutions.
Access Whitepaper
For queries connect directly with our experts at electrification@cyient.com
Information systems in the railway industry is on a new journey—towards an increasingly digital and virtual infrastructure. The focus is on improving asset availability and operational performance. Having a robust condition monitoring system for rolling stock is critical to ensure seamless functioning of the rail network, planning corrective maintenance actions, and proactively scheduling component replacements. Smart railway companies are effectively using big data analytics to monitor asset condition in near real time giving them greater control over their operations and significantly enhancing decision making.Download this paper to know how the Cyient data analytics team developed and implemented a comprehensive condition monitoring system for rolling stock by analyzing big data. Learn how terabytes of raw data generated across railway networks can be leveraged to ensure optimal functioning of rail assets, increase efficiency, improve safety, and streamline processes across the network.

Download the White Paper
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)