- 2026-Feb-17
The Place of Location Intelligence in a Sustainable Future
Written by Nihar Ranjan Sahoo 20 Mar, 2023
Sustainability isn’t just another buzzword to attract investors and position yourself as a thought leader across industries. It is a grave concern requiring our immediate and long-term focus. Increasing risk of global food shortage, natural disasters, global warming, water scarcity, and surging greenhouse gas emissions have hit the global population hard, resulting in:
- Around 800 million people living in extreme poverty, suffering from hunger
- 144 million people being displaced from their homes by natural disasters between 2008 and 2012
- Water scarcity affecting 40% of the global population and is projected to surge massively.
These issues are likely to multiply if not looked at through a sustainability lens. In a Deloitte survey on more than 2,000 C-suite executives, 79% said the world was at a “tipping point” in responding to climate change. Just 59% had felt that way a mere eight months earlier. However, optimism that immediate action can limit the worst of climate change has grown from 63% to 88%. One of the key ways to progress toward a sustainable future is by developing and utilizing spatial solutions to help meet the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Let us understand how one such solution, location intelligence, will drive focus toward sustainability, providing substantial data enabling the designing of smarter and greener cities.
Significance of location intelligence
Location intelligence (LI) builds on geographical information systems (GIS) tools, and its capabilities go beyond the analysis of geospatial or geographic information. It has the ability to visualize spatial data and to identify and analyze information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet that can be detected via remote-sensing technologies. The dependence on earth observation data (EO) collected from geospatial information is huge, especially when it comes to SDGs, as it relates people to their location and helps monitor progress at a specific region, district, state, or local level.
Location intelligence offers numerous business benefits, which include optimum efficiency and scalability, improved decision-making, and competitive advantage. Earth observation provides key data for monitoring land use, soil, snow cover, drought, and crop development. It also provides data on water cycles, air quality, forests and other aspects of the natural environment, and the epidemiology of infectious diseases, directly addressing most of the 18 SDGs identified by the UN. Listed here are some of the most sought-after advantages of leveraging this technology and implementing it in your business:
- Improved customer relationships: With accurate data collected using location intelligence, businesses can tailor products and services according to their customers’ needs and behaviors. These insights increase sales and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced supply chain operations: By identifying new market opportunities and making better decisions about site selection, LI can help businesses improve supply chain operations.
- Increased efficiency: Detecting location-based hindrances such as delays in order supplies or other bottlenecks that pose a threat to business efficiency becomes easier with LI.
- Real-time decisions: LI helps companies and businesses make decisions in real time, based on the latest and most accurate location data.
Location intelligence is used by organizations across industries to improve their business processes. Some of the top location intelligence use cases are:
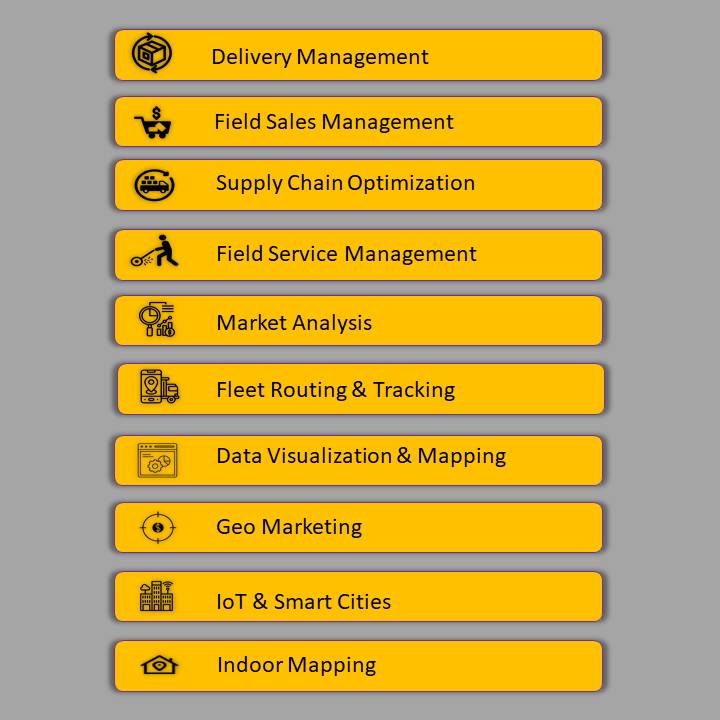
The role of geospatial in location intelligence
More than 90% of businesses believe location intelligence is critical to their success. They deliver location intelligence through geospatial data and spatial analysis, which enables comprehension, insight, decision-making, and prediction. Applications range from finding optimal retail site locations and resolving traffic bottlenecks to maintaining and repairing critical infrastructure. Location intelligence—powered by geographic information system (GIS) technology, machine learning automation, and done at scale in real time—is helping transform several industries. Leveraging geospatial data in location intelligence fulfills 11 out of the 18 UN SDGs:
- Eliminating poverty: GeoAI using earth observation data (temporal data) that provides soil, geology, hydrology, topography, and more, along with geocoded census data such as gender, age group, earning members, population, population growth, per capita earning, spends, and land ownership, provides a comprehensive view of potential areas that need attention for remediation and support.
- Eliminating hunger: GeoAI using earth observation data on crop variety, yield, growth, and forecasting from integrated analysis of data—soil, land use, hydrology, geologic parameters, and precision agriculture.
- Good health and well-being: Machine learning with geospatial data on healthcare systems, remote patient care, spatio-temporal analytics on epidemic forecasting, and disaster management planning and monitoring.
- Clean water and sanitation: GeoAI in potential groundwater resource mapping using EO data, ground truthing data of water table and geologic, geomorphological parameters, water quality data; site planning for artificial recharge structure, demand and supply analytics, locate point and non-point pollution sources and geo-environmental analytics.
- Affordable and clean energy: GeoAI-based multi-criteria assessment for rooftop solar PV deployment or perform a site suitability analysis for a new wind farm using EO data.
- Industry innovation and infrastructure: Select GeoAI use cases: assessing access to public transit, visualizing the expansion of public transportation, mappinging green infrastructure, monitor emissions, and assessing ICT infrastructure implementations.
- Sustainable cities and communities: GeoAI-based global mapping, modeling, and measurements of urban growth using EO data; urban planning and efficient usage of water, delineation of flood-prone land or open space to reduce flood insurance for communities.
- Climate action: Mapping of GHG, CFCs, and other hazards and forecasting analysis and mitigation planning for human lives.
- Life below water: Monitoring ocean pollution (oil spills and other), ocean temperature monitoring addressing marine pollution, protection of marine and coastal ecosystems, minimizing ocean acidification, regulating and managing fishing activities, prohibiting overfishing, increasing economic benefits to small islands via the sustainable use of marine resources, and identifying potential fishing zones.
- Life on land: GeoAI helps quantify forest cover, deforestation and forest degradation, forest biomass analysis, and carbon sequestration with earth observation and allied datasets.
- Space economy: GeoAI enables operational space weather data and forecasts, developing space weather models and tools, and collecting established practices on the mitigation of space weather effects.
How Cyient leverages location intelligence
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) has disrupted almost every industry and led to transformation in systems of production, management, and governance. It has connected billions of people across the globe with unprecedented processing power, storage capacity, and access to limitless knowledge. Digital infrastructure, which will define the next decade, has been making a significant impact in geospatial and space technology and on the five megatrends envisioned by Cyient - Industry 4.0 and Smart Operations, Intelligent Transport and Metamobility, Digital Healthcare, Sustainability, and Space Systems.
Digital infrastructure will exploit AI/ML, cloud, and IIOT and integrate with geospatial and earth observation capabilities to develop national geospatial knowledge infrastructure and its applications in almost every walk of life—agriculture, water, health, energy, land and property, digital cities, supply chain management— helping address SDGs.
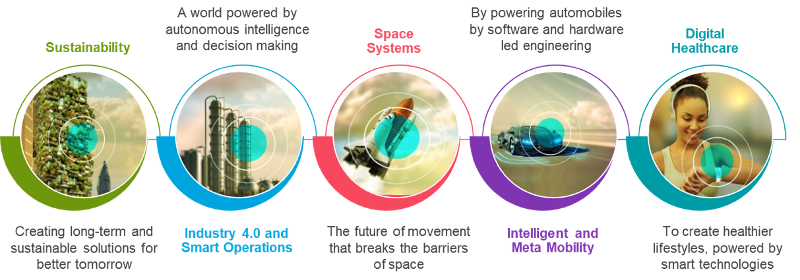
In addition, geospatial technology has been disrupting most industries, providing positive outcomes with location-based services along with automated workflows (pipelines) to enable decision-making, drive operational efficiency, and increased productivity with effective and efficient planning, execution, monitoring, and evaluation. Seamless integration of GIS with enterprise systems—ERP, CRM, SCM, asset management, work management, project portfolio management—along with sensory data, AI, and decision science provides a unified visualization platform for users anywhere, anytime. GeoAI, along with MLOps, is being deployed for automated execution of engineering workflows/pipelines.
Cyient has been enabling industries and the government to leverage the “power of location” in a number of ways: provisioning urban digital models that underpin smart cities; high-definition maps for autonomous vehicles; modernizing grids and network assets (optimizing network distribution management, network reliability, safety and resiliency, minimizing service disruption, predictive maintenance and support); providing Smarthub in mobile field inventory management; real-time dynamic scheduling and optimization of rail services for emergencies; vegetation analysis for encroachments on utility lines; 5G network design and rollout; and underground and overground pipeline integrity management.
About the author
Nihar R Sahoo is a Ph.D. in Earth Sciences specializing in GIS, Remote Sensing, and Applied Statistics. He has over 23 years of industry experience. His areas of interest are building end-to-end development, deployment, and operationalization of geospatial machine learning solutions with earth observation data.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




