- 2026-Feb-17
SmartHub: Geospatial Field Inventory Management
Written by Cyient 05 Dec, 2023
With digital transformation strategies, real-time location intelligence is essential for enterprises across sectors to explore how spatial information can help enhance collaboration and serve their customers anytime from anywhere. An Enterprise Geographic Information System (GIS) across industries typically requires a field inspection solution for organizations to manage, analyze, and visualize geographic and spatial assets through mobile devices with real-time updates while ensuring the system maintains a single source of truth. This solution allows field personnel, remote workers, and other stakeholders to access and interact with spatial information while on the go.
Need for a Field Inspection System
Lately, there has been tremendous potential for a field solution across industries as a part of the digital transformation journey. There are several reasons for this:
- Increasing use of self-service modules to enable real-time updates and increase operational efficiency and productivity.
- Mandatory on-site inspections for high-priority cases or those that require third-party reviews.
- Rise in digital checklists and automated inspection reporting for increased operational efficiency.
- Configurable workflow integration and real-time updates to provision a seamless execution of tasks with efficacy.
- Rising use of cloud-based SaaS solutions to provision an enterprise-wide unified system with seamless integration.
- Ground truth collection in geospatial model training and validations—a promising feature, as it captures the coordinates and attributes.
Solution
A field GIS solution comprises a set of features that provides users with a map viewer from a mobile device, which could be on Android, iOS, or on Windows, to view, edit, and collect spatial data; it provides associate attribute information that is collected from the field; and updates the data in the enterprise geospatial- asset management system or an ERP. Key components and features of an enterprise GIS Field solution typically cover the following:
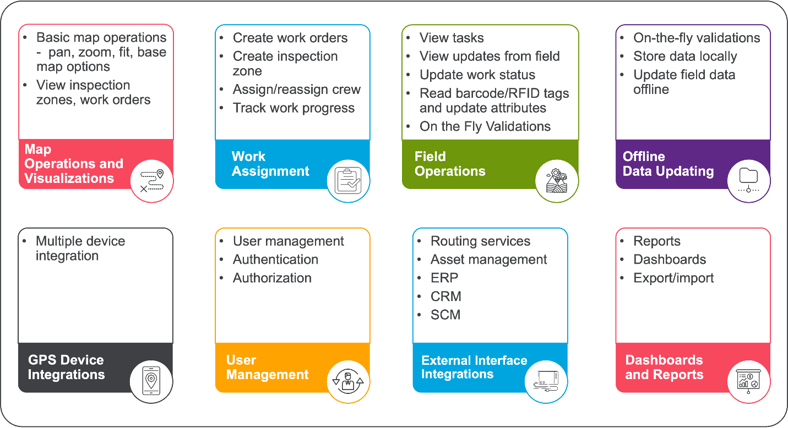
- Map operations and visualizations: Allow the field crew to view inspection locations with basic features of pan, zoom, fit, measuring distances, areas, and buffering around features, study the terrain and carry out inspections effectively and efficiently, and visualize trends or patterns in the collected data.
- Work assignment: Allows supervisors and dispatchers to schedule work plans for field staff with a work order and inspection zone, assign crew to attend, set date of visit, and more. The field crew can update the status in real time. This gets tracked on a daily basis and presents a dashboard of work performance.
- Data collection and editing: Real-time data sync using GPS-enabled devices to capture points, lines, and polygons, and attributes, including attaching photos, voice, video, and notes to specific locations. This ensures that inspection data is backed up and can be accessed from various devices and available from anywhere anytime.
- Offline capabilities: In areas with poor or no Internet connectivity, this enables users to work offline and sync data once back online or in the office.
- Customizable workflows: Covers custom forms, data validation, and automated processes, along with review and validation of primarily offline data and work progress.
- Customizable checklists: Offers customizable inspection checklists based on industry standards and specific requirements. Inspectors can follow these checklists to ensure consistent and thorough inspections.
- Integration with back-end systems: Can integrate with back-end systems such as asset management, maintenance, or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to streamline data sharing and further workflows. This typically integrates with the shortest and optimal route planning and operations tool for field crew or spare parts delivery and scheduling for outage restoration.
- Reporting and dashboards: Generates comprehensive and customizable inspection and work performance reports. These reports can include collected data, photos, videos, location information, and any annotations made during the inspection.
- Notifications and alerts: The solution is capable of sending real-time alerts or notifications to relevant stakeholders based on inspection outcomes or specific criteria.
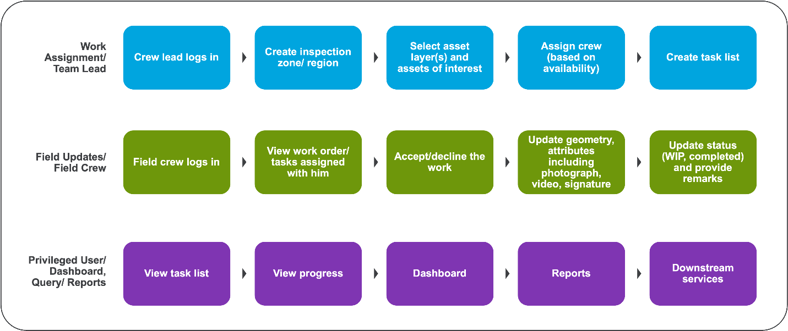
A high-level workflow for key functionality:
Non-functional Features
- Compatibility and interoperability: Works seamlessly with legacy IT-GIS platform within the organization.
- Scalable to handle increasing data volumes and user demands as the organization grows.
- Extendibility in terms of enhanced functionality.
- Performance: Publishes or presents results with minimal or no latency.
- Security: Protects against unauthorized access and data breaches, protects data both in transit and at rest.
- Usability: Provisions easy navigation, minimal user input, and seamlessly integrated functionality.
Engagement
Implementing an enterprise GIS mobile solution brings in several benefits—improved efficiency in field operations, better decision-making based on real-time data, reduced manual data entry errors, and enhanced collaboration between field and office teams, leading to increased productivity. It also ensures regulatory non-compliance if any to safety, environmental, and other local regulatory parameters by having automated validations during field operations.
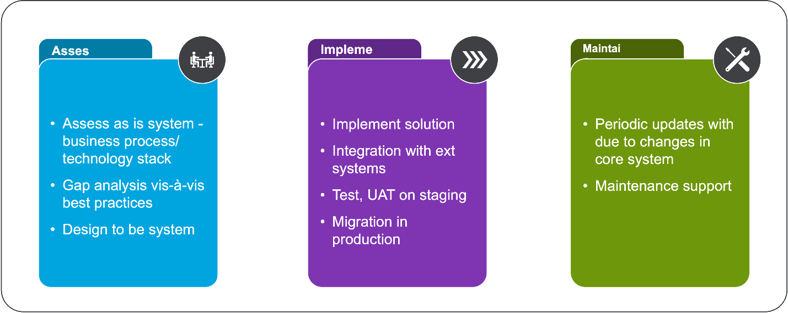
When considering or implementing such a solution, it's important to customize specific industry needs and operational workflows. It would, however, require careful planning, alternate solutions in integration with legacy systems, and consideration of factors such as device compatibility, data security, and user experience while trying to improve efficiency, accuracy, and data-driven decision-making in field updating processes. A typical engagement with the customer would be in the three phases shown below.
Cyient has been delivering geospatial solutions for over 30 years for utilities, telecom, and mining and has implemented field solutions on the Esri Platform for 10+ utility clients. Smart Hub is platform-agnostic and is deployable by extending any geospatial legacy system with customers. This solution has been deployed for over a dozen utilities and telecom customers.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




