- 2026-Feb-17
Journey of Transformation: Implementing an Outage Management System
Written by Cyient 27 Dec, 2023
In the swiftly evolving landscape of electrical utilities, staying ahead requires adopting cutting-edge technologies to ensure reliability, resilience, and customer satisfaction. Metrics like the System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI) and System Average Interruption Frequency Index (SAIFI) are important considerations in this context. Regulatory standards frequently define benchmarks for SAIDI and SAIFI, aiming to guarantee a specified level of service reliability for consumers. A crucial step in this development is the incorporation of an outage management system (OMS).
The OMS is instrumental in efficiently handling outages by serving as an integration platform for all systems and processes responsible for power supply-related issues. By incorporating customer calls, AMI events, robust prediction engines, and real-time SCADA information, the OMS can anticipate potential outage locations on field devices. This leads to quicker problem resolution and optimal crew dispatching. Real-time crew availability ensures efficient dispatching, allowing the closest available crew with the right expertise, equipment, and materials to address the outage promptly. This blog details the implementation journey of an OMS in an electrical utility, offering broader insights into the challenges faced, strategies employed, significant impact on SAIDI, SAIFI, outage response, and lessons learned.
Understanding the need for an OMS
Within the dynamic realm of electrical utilities, ensuring a dependable and continuous supply of power is a crucial goal. With the ongoing surge in electricity demand propelled by technological progress and a growing dependence on electronic devices, the complexities of addressing and mitigating power outages intensify. Acknowledging these challenges, an electrical utility identified the need for a comprehensive solution to elevate outage management and enhance overall grid reliability.
Traditional methods of outage management, which were reactive and time-consuming with crew manually responding to locate the fault, could not keep pace with changing demands. As the electric utility landscape got more complex, the integration of renewable energy sources, the expansion of smart grid technologies, and soaring expectations of consumers for uninterrupted service needed a transformative approach. The decision to implement an OMS was a strategic response to modernize outage response, reduce downtime, and elevate the quality of service provided to customers.
Strategic planning and stakeholder collaboration
The implementation process kicked off with a detailed planning phase, where strategic considerations included thorough analysis of existing outage management procedures, active involvement of stakeholders, and close collaboration with technology vendors. As part of this comprehensive strategy, specific goals for SAIDI and SAIFI were established.
A meticulous project plan was developed, addressing key elements of timelines, resource distribution, and risk assessments. Stakeholders from various departments, including field crews, IT, and customer service, played a crucial role in ensuring the seamless integration of the outage management system with diverse operational requirements, aligning it with the objectives for enhanced service reliability.
The success of this planning phase relied on the collective efforts of stakeholders in defining project objectives, setting timelines, efficiently allocating resources, and strategically incorporating SAIDI and SAIFI goals. This approach also laid the groundwork for a system that aimed to enhance both operational efficiency and overall service reliability.
Execution challenges and adaptive strategies
In the execution phase, resistance to change among field personnel presented a notable challenge. Engaging and addressing the concerns of those directly involved in the day-to-day operations was crucial for a smooth transition.
Ensuring a seamless transition from manual to automated processes was a critical aspect of the execution phase. User training programs were implemented to equip personnel with the necessary skills to navigate the new system, fostering acceptance of and ability to utilize the advanced technology.
Continuous communication played a vital role in addressing emerging and unforeseen challenges. Regular updates and open channels of communication helped build a shared understanding of the ongoing changes, fostering transparency and cooperation.
The responsive approach adopted during execution swiftly addressing any unexpected issues, was instrumental in maintaining momentum and gaining the support of end-users. By promptly resolving concerns and adapting strategies based on real-time feedback, the implementation process remained adaptable and effective.
Integration with existing systems
The integration of the OMS with existing systems, including supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), geographic information systems (GIS), customer information systems (CIS), etc., presented notable challenges in achieving seamless collaboration. The primary objective was to ensure a smooth flow of data among these systems, emphasizing interoperability, synchronization, and compatibility throughout the process. This required extensive collaboration between the organization's IT team and the OMS vendor to establish a unified and interconnected infrastructure.
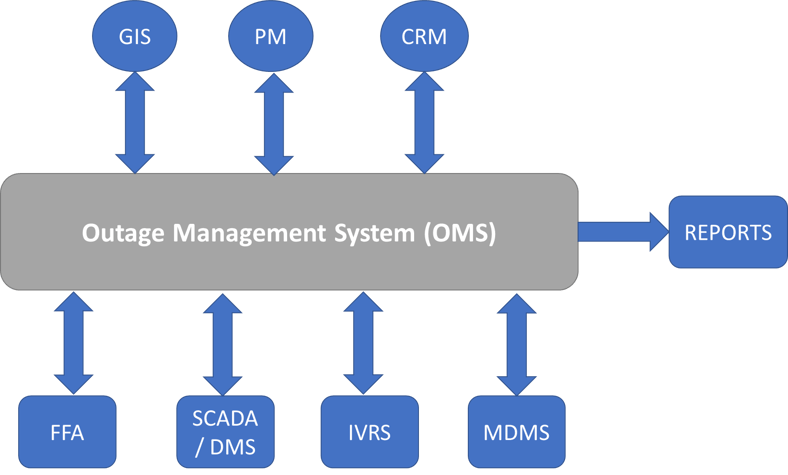
A comprehensive integration approach was crafted to address these integration challenges. The approach involved developing robust data interfaces that facilitated the smooth exchange of information between the OMS and existing systems. This ensured that data from existing IT/OT systems seamlessly interacted with the OMS, creating a consistent network that enhanced our overall operational efficiency. Regular checks and updates were implemented to maintain synchronization, enabling real-time data sharing and decision-making.
Further, enhancing compatibility involved implementing custom solutions designed for the particular needs of each system. Collaborative efforts with the OMS vendor and utility IT teams helped establish protocols and standards, enabling the efficient integration of various systems. This strategic alignment not only tackled integration challenges but also established the groundwork for a well-coordinated and synergized technological infrastructure.
Deployment—minimizing downtime, maximizing efficiency
The deployment phase required a careful balance between the need for quick implementation, thorough testing, and validation processes. Prioritizing the reduction of downtime, assuring the reliability of the system, and implementing comprehensive training programs for end-users were critical elements of this stage. The challenges encountered highlighted the significance of a well-coordinated approach to prevent disruptions to daily operations.
A strategic deployment plan emphasizing a phased implementation approach was the answer. This allowed for systematic testing and validation at each stage, ensuring that the system was not only swiftly put into action but also thoroughly examined for functionality and reliability. Minimizing downtime was achieved by strategically scheduling the deployment to minimize the impact on regular operations.
Extensive training programs were conducted to empower end-users with the necessary skills and familiarity with the new system. This proactive approach aimed at facilitating a smooth transition and ensuring that personnel were proficient in utilizing the deployed technology effectively.
Throughout the deployment phase, the focus remained on maintaining a well-coordinated approach involving clear communication and collaboration among all stakeholders. This strategy ensured that the implementation process did not disrupt the routine operations of the electrical utility.
Lessons learned from implementation
Valuable lessons were gained through the OMS implementation that significantly enhanced operational excellence.
- One crucial insight was the importance of the early involvement of stakeholders, right from the planning phase. This approach ensured that the OMS aligned with their needs and minimized resistance during the implementation process.
- The quality and quantity of data was another critical factor, underscoring the need to have accurate and sufficient information to enhance the system's functionality.
- A dedicated project team and close collaboration with the OMS vendor became crucial, emphasizing the value of effective partnerships in navigating challenges and achieving success.
- Continuous communication, regular feedback loops, and a commitment to real-time issue resolution emerged as fundamental practices, fostering adaptability and efficiency.
- Additionally, the experience highlighted the necessity of strategic deployment planning, balancing urgency with meticulous testing to minimize downtime and ensure system reliability.
Overall, the implementation process emphasized the importance of a collaborative culture, ongoing improvement, and proactive problem-solving in enhancing the effectiveness of an outage management system for utilities.
Resilient future for electrical utilities
The introduction of an outage management system went beyond mere technological enhancement; it signified a strategic advancement toward a more robust and customer-focused electrical utility. The system's capacity to identify, assess, and promptly address outages in real time has not only optimized outage management but also positioned the utility to actively navigate the ever-changing energy environment. The OMS provide forward-looking capabilities, plotting a course for a utility that not only meets present needs but also stays ahead in tackling the evolving challenges and opportunities in the energy landscape. This ensures a more sustainable and dependable energy future for all stakeholders.
Cyient has been supporting utility companies across geographies in overcoming the challenges mentioned above to ensure a smooth OMS implementation. Our competency includes addressing issues such as data flow from legacy to new systems, ensuring seamless integrations with existing IT/OT infrastructure, maintaining robust data governance, safeguarding systems against online threats, and managing changes while building capacity for utilizing new technologies.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




