Bluetooth -A Smart Communication Protocol for the Internet of Things
Written by Narendra Sivalenka 24 Mar, 2017
Picture this. You are sitting in your garden, but you are able to draw out the blinds in your house or open the door for a visitor with the help of your smartphone. Or in an industrial scenario, you are able to connect thousands of IoT devices without large deployment hubs. These are just some examples of what IoT can do for individuals and businesses.
However, to realize IoT’s potential, standardized communication protocols are needed. Recent developments in Bluetooth are set to position the technology as ‘the communication protocol of choice’ for IoT. According to Bluetooth Specialist Interest Group, by 2020, more than one-third of all installed IoT devices will be Bluetooth-enabled. In fact, Bluetooth with its ability to connect disparate devices and industries through short-range technology can transform the way devices interact with each other.
Today, Bluetooth technology has evolved from classic Bluetooth to smart Bluetooth stage, including the latest version Bluetooth 5. For instance, Bluetooth 5 has four times the range, double the speed, and 800% more data broadcasting frequency, as compared to its earlier versions. These enhanced features, will increase the number of applications for which Bluetooth will be a smart choice as companies with large and critical infrastructure can have 100% uptime and cost effective solutions by deploying Bluetooth 5 enabled IoT devices. In addition, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), a version of Bluetooth designed for low-powered devices can help IoT devices conserve energy by maintaining the devices in sleep mode-until they are connected. What makes BLE ideal for IoT applications is the fact that it can rapidly pair and reconnect with devices in six milliseconds-down from six seconds for classic Bluetooth. This not only helps in enhancing operational efficiency but also improving device availability.
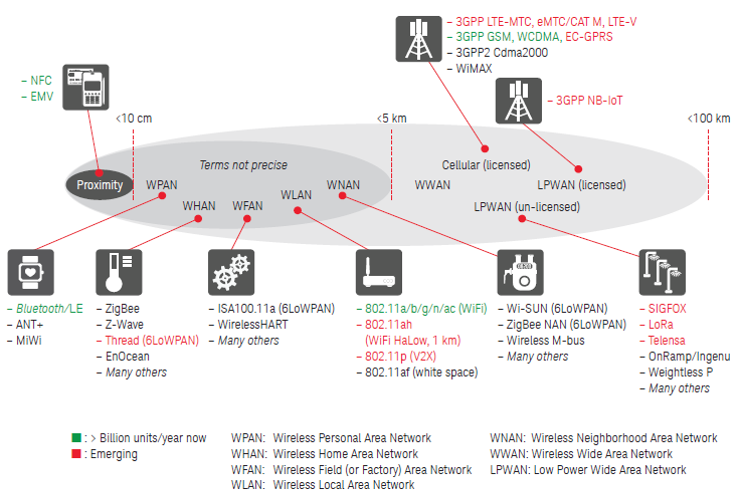
Figure 1: Snapshot of communication protocols grouped by standards, frequency, range and data transmission rates
Source: Keysight Technologies
How Bluetooth Enhances the IoT Architecture
A typical IoT architecture consists of hardware, communication, software system and application layers, with Bluetooth acting as the communication layer. The communication layer is a critical bridge between the layers and consists of a multi-layer stack, including data link, network or transport, and session protocols (see Figure 2). Bluetooth or BLE is part of the data link layer, which connects either sensor to sensor or sensor to the gateway. The network layer, on the other hand, is responsible for routing or moving packets across the network, using the most appropriate paths. The session layer protocols enable messaging across various elements of the IoT communication subsystem.
As compared to other communication protocols such as RFID, NFC, WLAN, LoRa WAN, LTE-A, WiFi-Direct (see Figure 1), Bluetooth technology is less costly to deploy. It also enables wireless connectivity and creates instant Personal Area Network (PAN) where wireless infrastructure is not available. It has low interference and a standardized protocol. Not only that, Bluetooth’s typical range of 0-30 meters can be increased by amplifying the power beyond one milliwatt (mW).
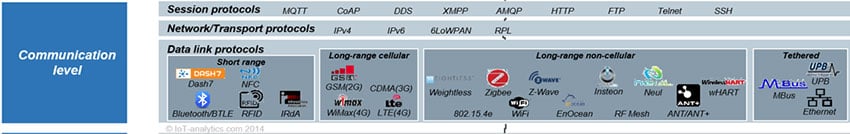
Figure 2: Data link protocols
Taking IoT Connectivity to the Next Level
Bluetooth enabled IoT applications are being increasingly used across industries under the themes of Asset management, Safety and Worker health, including healthcare, automotive, home and entertainment, and security. With IoT market estimated to grow from USD 157.05 billion in 2016 to USD 661.74 billion by 2021, Bluetooth-powered IoT can be a big differentiator for companies looking to reduce manual tasks and enhance operational efficiency. Organizations with a well-planned IoT strategy and a deep understanding of use cases and technology protocols can establish new forms of machine-to-machine and machine-to-human communication, thereby driving superior experience and customer delight.
Glossary
Bluetooth: A short range wireless communication technology for exchanging data using short-wavelength UHF radio waves (2.4 to 2.485 GHz) and build personal area networks (PANs).
IoT: Internet of Things (IoT) - at times referred as Internet of Everything - is the network of physical objects or ‘things’ embedded with electronics, software, sensors and connectivity, enabling objects to exchange data over the internet
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)