- 2026-Feb-17
Building a Sustainable Future: Cyient & IBM in Energy Utilities
Written by Pankaj Kumar Sahu 07 Nov, 2024
Cyient, a global engineering and technology solutions company, has partnered with IBM, a leader in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data management. IBM's Envizi tool automates ESG data capture and management, empowers organizations to accurately calculate Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, streamline sustainability reporting, and identify decarbonization opportunities.
As climate change necessitates urgent action, the Energy & Utilities sector - one, of the largest contributors to GHG emissions, is undergoing a significant transformation. This blog discusses the key sustainability factors within the industry, the steps utilities are taking toward greener operations, and the essential role of IT implementers and system integrators, highlighting IBM Envizi's capabilities.
Sustainability Drivers for Utilities
The Energy & Utilities sector is at a pivotal moment, where sustainability is not just a goal but a necessity driven by global commitments, regulatory mandates, and growing stakeholder expectations. As the world races towards decarbonization, utilities must navigate an evolving landscape that demands innovative solutions, transparency, and accountability to achieve a sustainable future. This section explores the key drivers propelling utilities to embrace sustainability and reshape their operations for a cleaner, greener world.
Global Decarbonization Commitments
Global decarbonization efforts, driven by agreements like the Paris Agreement, are transforming the Energy & Utilities industry. Over 120 countries have committed to net-zero emissions by mid-century, fueling a surge in investments in green technologies. The global green hydrogen market was valued at USD 6.42 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 84.03 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 53.53%. Similarly, the carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 12.6% during this decade.
Utilities are increasingly adopting innovative technologies like green hydrogen, carbon capture, and advanced nuclear reactors to meet these ambitious targets. As the industry accelerates its decarbonization efforts, these technologies are becoming critical in ensuring a sustainable and low-carbon energy future.
New Regulations
Governments worldwide are increasingly enforcing regulations to curb emissions and promote renewable energy. In the EU, the European Green Deal and Climate Law require member states to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030. This regulatory push is driving substantial investments in green energy, with the EU committing €1 trillion towards sustainability initiatives by 2030.
These regulations are compelling utilities to enhance transparency and accountability. For example, one of Europe’s largest utility companies, has committed to investing €190 billion by 2030 in renewable energy and decarbonization efforts as part of its strategic plan to align with EU regulations. Such investments are crucial as utilities transition to renewable energy sources, ensuring compliance with mandates and contributing to a sustainable energy future
Stakeholder Pressure
Investor pressure is reshaping the utilities sector as ESG-focused investing gains momentum. Investors are increasingly prioritizing companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, pushing utilities to adopt sustainable strategies to secure access to capital and enhance their market position.
Consumer expectations are also evolving, with environmentally conscious consumers demanding cleaner energy. According to a Deloitte study, 68% of consumers now prefer renewable energy sources, and 54% are willing to pay a premium for clean energy. Utilities that respond to this demand by offering renewable options are rewarded with increased customer loyalty, driving both brand value and long-term growth.
The Path to Sustainability: From Leadership Vision to Opportunity Realization

- Leaders’ Thought Processes
Utility leaders now consider sustainability as a strategic imperative. Integrating sustainability into core business strategies is crucial for long-term success. Leaders are partnering with regulators, technology providers, and stakeholders to ease the transition to a sustainable energy system.
- Challenges
- High Costs of Renewable Infrastructure
Transitioning to renewable energy requires substantial upfront investment, presenting financial challenges, particularly in regulated markets.
- Regulatory Compliance
Navigating complex regulations demands considerable resources, with compliance requirements varying across regions.
- Workforce Transformation
The shift to sustainability necessitates new skills and talent, compelling utilities to manage workforce transformation while maintaining ongoing operations.
- High Costs of Renewable Infrastructure
- Opportunities
- Technological Innovation
Investing in smart grids, energy storage, and digital platforms can provide utilities with a competitive edge while advancing sustainability goals.
- New Revenue Streams
Utilities can generate new revenue streams by offering energy-as-a-service and participating in carbon markets, helping to offset the costs of the sustainability transition. Enhanced Brand Reputation Leading in sustainability strengthens brand reputation, attracting customers, investors, and fostering positive relationships with regulators.
- Technological Innovation
- Transitioning to Sustainability
Transitioning to sustainability involves a comprehensive transformation of a utility’s operations, business model, and culture. A strategic roadmap guides this process, outlining key steps and milestones. The diagram below highlights the key components essential for utilities in their transition to sustainability.
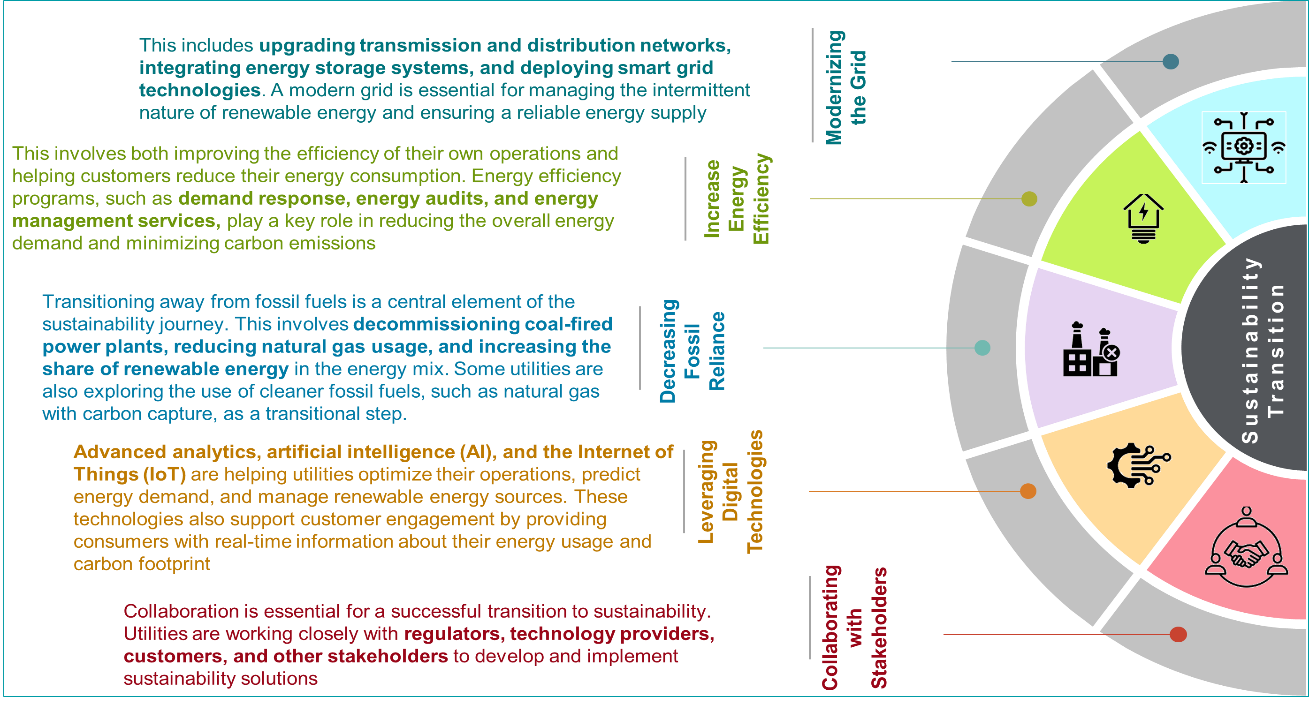
Cyient’s Viewpoint on Sustainability Development
A system integrator plays a key role in guiding a utility’s sustainability journey by developing a clear, actionable strategy in close collaboration with the utility. This strategy is aligned with the utility’s business objectives and sustainability goals, providing a comprehensive roadmap for implementing sustainable practices. The diagram below outlines a step-by-step approach to sustainability development for a utility.

Sustainability Solutions for Utilities Leveraging IBM Envizi
Cyient leverages IBM Envizi to provide a comprehensive suite of sustainability solutions for utilities, helping them manage their environmental impact, comply with regulations, and achieve sustainability goals.
Key Features of Envizi ESG Solution:
- Environmental Data Management: Collect and manage data on energy consumption, emissions, water usage, and waste, providing a holistic view of environmental impact.
- Regulatory Compliance: Tools for tracking and reporting sustainability metrics, ensuring compliance with global standards like the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol and Task Force on Climate Related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) ESG reporting framework.
- Carbon Management: Track carbon emissions, set reduction targets, and develop strategies for achieving them, including carbon offsetting.
- Energy Efficiency and Optimization: Tools for optimizing energy efficiency, supporting energy audits, demand response programs, and energy management services.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Customizable reports and dashboards to communicate sustainability performance to investors, regulators, customers, and employees, building trust and demonstrating commitment.
How are we Capturing, Consolidating, Analyzing the Sustainability Data using Envizi Platform?
The IBM Envizi platform automates the collection and consolidation of more than 500 data types and supports major, internationally recognized ESG reporting frameworks.
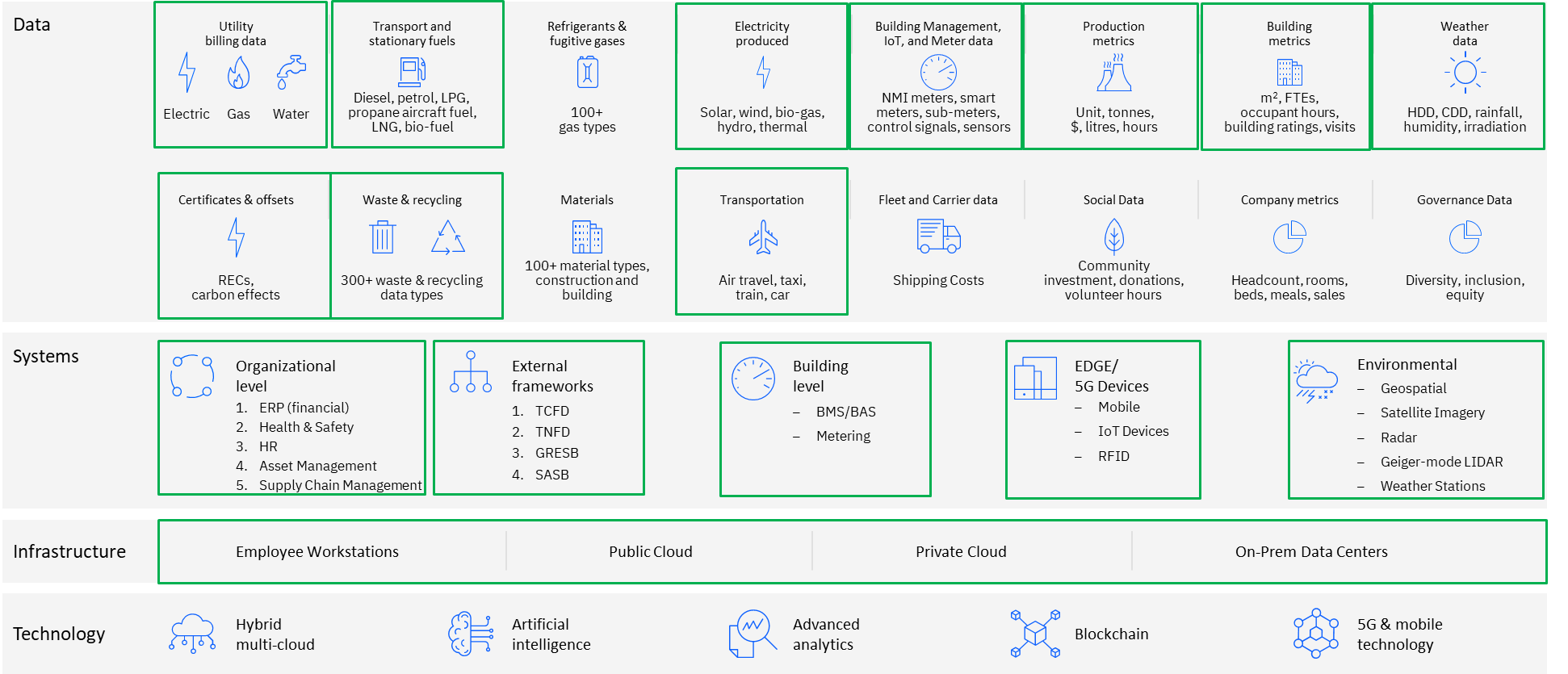
Envizi Solution Platform Modules
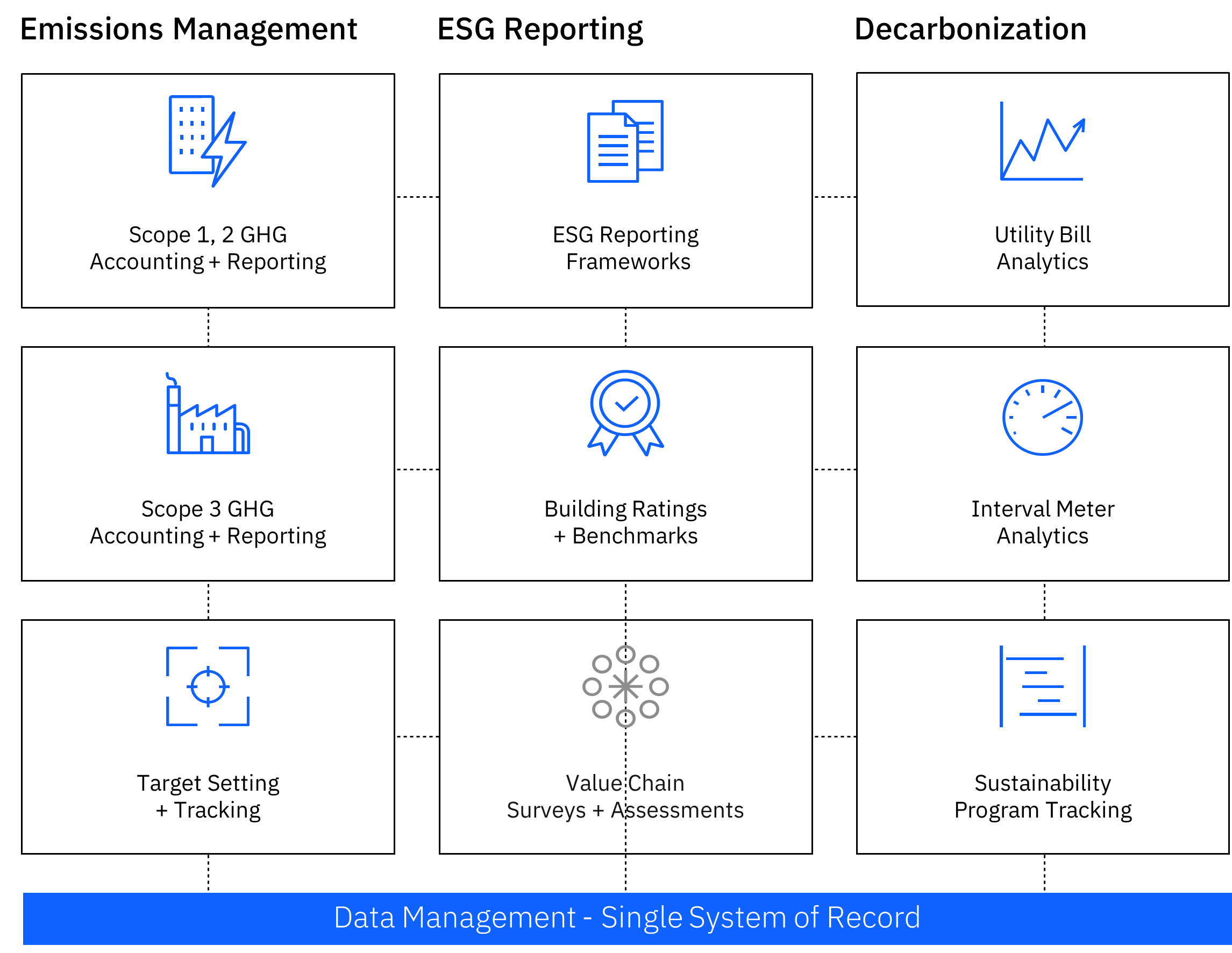
The Envizi Solution Modules depicted in the diagram below is structured into nine modules, categorized under three core solutions: Emissions Management, ESG Reporting, and Decarbonization.
Emissions Management: It helps utilities and businesses track, manage, and report greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across their operations. It enables real-time monitoring, providing the data needed to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and meet sustainability targets. It includes modules for:
- Data collection and integration from various sources
- Emissions calculation using standardized methodologies
- Scope 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions accounting and Reporting
- Target Setting and monitoring
ESG Reporting: It offers robust tools for streamlining and automating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting. It allows organizations to efficiently collect, validate, and report ESG data, ensuring transparency and helping meet stakeholder expectations. Modules in this area covers:
- Data aggregation and validation for ESG metrics
- ESG Reporting framework alignment (e.g., Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), TCFD)
- ESG building benchmarks and ratings (e.g. Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark (GRESB)
- Value chain assessments and surveys (Securely capture ESG data from third parties for value chain analysis)
Decarbonization: It focuses on reducing carbon footprints through targeted strategies. By leveraging detailed data insights, utilities and businesses can develop and implement effective decarbonization plans, accelerating their journey towards net-zero emissions. The modules include.
- Utility Bill Analytics (Analyse and report utility bill costs, consumption, savings etc.)
- Interval Meter Analytics (Consolidates data from utility meters and sub-metering systems to simplify and standardize granular monitoring of utility demand and consumption)
- Sustainability Program Tracking (Expands beyond emissions reduction and energy efficiency to monitor sustainability projects like waste diversion, water reduction, and recycling, scenario modelling etc.)
Conclusion
The Energy & Utilities industry stands at a critical juncture, with sustainability becoming central for long-term success. Utilities must navigate challenges such as high costs and regulatory compliance while embracing opportunities in technology and new revenue streams. Leaders who prioritize sustainability will drive innovation, enhance their brand reputation, and secure a competitive edge in a rapidly changing market. Cyient is playing a crucial role in this transformation by providing utilities with robust ESG solutions through IBM Envizi, helping them manage environmental data, ensure regulatory compliance, and achieve their sustainability goals. As the industry transitions to a greener future, collaboration and strategic planning will be essential to achieving sustainable growth.
About the Author

Pankaj Kumar Sahu, Director, Enterprise Asset Management Practice, DTG
Pankaj Sahu spearheads the Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) practice for Electric, Gas, and Water Utility technology solutions at Cyient. With a wealth of experience spanning over 20 years, he has an established track record in implementing and consulting EAM and APM solutions for clients in the Utility, Transportation, and Energy sectors worldwide.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)




