AI in Screening, Diagnosis, and Healthcare Management
Written by Vishwanath Pratap Singh 24 Mar, 2023
Maintaining good health has become an integral part of our lives, and with technology constantly nudging us through numerous health apps and tools, making the right lifestyle choices has come into sharp focus. While there is an ongoing debate about how technology has adversely impacted our health, let us consider the flipside of digital healthcare and look at its positive outcomes. From monitoring our daily habits and calorie counting to keeping tabs on our mental health, digital well-being has come a long way, and our dependence on it is only poised to grow.
Health Management Cycle
Preventive health is the first step in the overall health management life cycle. We can achieve optimum health only when we take control and become mindful of our lifestyle choices. However, several factors and dynamic processes affect disease and disability, ranging from environmental factors to genetic predisposition to disease agents. Once you have a health concern, the next steps kick in: early diagnosis and monitoring and management of health.
Digital healthcare demand is driven by an aging population, higher patient expectations and participation in healthcare, and changing lifestyles, with healthcare professionals being responsible to meet demand, supply, and regulatory compliance. With increased dependence on digital healthcare, the need to identify and mitigate the gaps in supply and meeting the quality expectations of patients has become imperative.
While automation and digitalization have added great value to the healthcare industry, they have also created new risks and challenges for regulators. For example, the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in decision-making processes may lead to biased or discriminatory outcomes, which could undermine the fairness and integrity of the regulatory process. To address these challenges, regulatory bodies need to develop new skills and capabilities to effectively use automation and the latest technologies in their operations. This includes investing in training programs and developing new frameworks for assessing and mitigating risks associated with these technologies.
Overall, the impact of significant innovations on the supply side on the regulatory cycle is complex and multifaceted, and will require ongoing attention and investment to ensure that the regulatory process remains effective and efficient in the face of rapidly evolving technologies.
How AI/ML and Robotics Facilitate the Three A’s of Healthcare
The three A’s of healthcare—Accessibility, Availability, Affordability—are crucial in health management. Striking the right balance between all three indicates that a country’s healthcare system is at peak performance. However, the availability of and accessibility to experts is in short supply, adding to rising healthcare costs. Several factors are at play in determining the cost of healthcare. These include sophisticated solutions, modernization of healthcare organizations, increasing cost of medical device R&D and pharma, along with stringent regulatory requirements and a long certification and approval process.
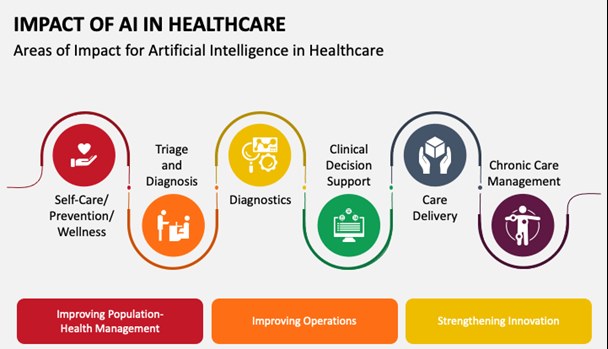
Digitized healthcare presents numerous opportunities for reducing human error, improving clinical outcomes, tracking data over time, making healthcare cheaper and more. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)-based automation can address some of the challenges common to the healthcare industry. Let us look at some of the most advantageous outcomes that can help revolutionize the healthcare space:
- By providing quantitative support in clinical decision-making, ML algorithm and deployment in the cloud and at the edge help in accurate decision-making. Machine learning statistical models define the correct parameters based on older use cases that were assessed by experts, resulting in accurate diagnosis of an ailment. This reduces the healthcare provider’s time and effort, increasing their availability for graver cases.
- Automating the process of a patient’s journey—scheduling appointments, patient registration, personalizing care, updation of electronic health records (EHR), and generation of prescriptions based on voice commands and discussion with the patient—helps doctors focus on the patient's issues, treatment, progress, and health outcome.
- The pandemic created an unprecedented need for telehealth services, which were otherwise the last choice for patients. In-person consultation was always preferred, as it allowed for better diagnosis and prognosis. However, telehealth supported by cloud technologies and AI changed how we looked at medical care by providing badly needed support to remote patients for whom accessibility was a significant concern.
- Advancements in medical imaging, such as automated image interpretation in radiology and pathology, boosted the efficiency and efficacy of healthcare organizations, with diagnoses based on peer-reviewed journals and fused with ML models to simulate a physician’s thinking. This also facilitates understanding the patient’s current and past condition, correlating with familial history, pathology reports, scanning reports, and combining this information to arrive at a holistic diagnosis and treatment plan.
- AI supported by medical data acquisition from the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and cloud technologies helps manage and extract useful information from the data presenting an opportunity to collaborate and engage with the patient directly.
- With multiple wearable sensors integrated with AI technology available seamlessly, capturing early signs of the patient’s health condition and avoiding unprecedented situations with timely alerts becomes possible, especially in conditions such as sleep apnea and heart arrhythmia. Adherence to medication and correlating evidence of medication and outcomes provides qualitative analysis support to clinical trials for greater accuracy, accelerating time-to-market for new drugs or devices.
- Robotics in healthcare is improving care delivery. With advancements in AI technology, robots have become more competent and are currently helping perform robotic surgeries, enabling faster recovery and better outcomes. Remote surgery is a reality and will soon become routine with the maturity of AI models and robust communications networks.
Accelerated Learning
Healthcare professionals have a deep learning curve, and there is significant pressure on highly experienced professionals. AI assists experts in being more productive while enhancing the quality of relatively new professionals by helping them catch up with experts faster, leading to accelerated learning. Automated systems are helping patients to triage their doubts and collaborate on digital healthcare platforms such as “patientslikeme” by sharing their information with patient communities, drawing on peer support, health insights, and more to manage their health. Defining how pivotal digital healthcare is becoming, our Megatrends report draws attention to adopting these technologies in transforming the healthcare industry. Given the scale at which AI/ML is accelerating in the medical field, the focus of healthcare organizations must shift rapidly to digital to stay ahead of the curve.
About the author
Vishwanath Pratap Singh, Industry Offering Head, Healthcare and Life Sciences, works with large number of customers to understand the business context and provide optimal and customized solutions.
.png?width=774&height=812&name=Master%20final%201%20(1).png)